Smooth Sumac
Scientific Name: Rhus glabra L.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | RHGL |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | ShrubTree, |
| Native Locations | RHGL |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Scarlet sumac
Uses
Ethnobotanic: This was a widely used species among Native American tribes. The uses included the making of a root and leaf tea to treat diarrhea, dysentery, and mouth/throat ulcers. The leaves of the plant were smoked for asthma. The blossoms were used by the Chippewa in a mouthwash for teething children. Comanche children enjoyed the sour acid taste of the fruits and leaves were added to tobacco for smoking by adults. Dye was also created from various parts of the smooth sumac. The fruits were used to make red dyes and the inner bark used to make yellow dyes.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Weediness
This plant may become weedy or invasive in some regions or habitats and may displace desirable vegetation if not properly managed. Please consult with your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, or state natural resource or agriculture department regarding its status and use. Weed information is also available from the PLANTS Web site at plants.usda.gov.
Description
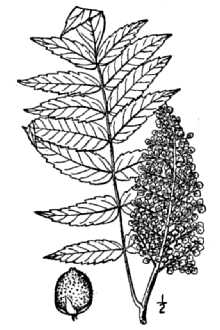
General: Sumac Family (Anacardiaceae). Smooth sumac can be a shrub or small tree growing up to 3 meters in height. Smooth sumac forms thickets from root suckers. The stems and branches are hairless and covered with a whitish waxy coating. The leaves are alternate and pinnately compound (3-5 dm long). Smooth sumac has 11-31 leaflets that are lanceolate to oblong-lanceolate (7-9 cm long). The leaflets taper to a point at the tip and are rounded at the base. The margins are sharply serrated. The upper surface is dark green and lustrous. The lower surface is covered with a whitish waxy coating. Smooth sumac has a branched, racemose inflorescence with flowers maturing from the bottom up (10-25 cm long). The flowers have a greenish color. The drupes have a flattened-globe shape (3.5-4.5 mm long) and are covered with red, sticky hairs. The seeds are yellowish in color and smooth (3-3.5 mm long). © Paul L. Redfearn Jr. Ozarks Regional Herbarium Distribution: For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Smooth sumac is found in open woodlands, prairies, on dry rocky hillsides, and in canyons.
Adaptation
Smooth sumac vigorously resprouts from rhizomes following fire. The rhizomes are usually located between 3 and 12 inches below the soil surface and this may provide protection from heat during a fire.
Establishment
Propagation of smooth sumac can occur by use of seeds or root cuttings. Seeds germinate best when exposed to continuous light and alternating warm and cool temperatures. Smooth sumac grows best in poor, well-drained soils, with partial to full sun. However, smooth sumac is a hardy species and will tolerate many soil types including soil that is slightly saline.
Pests and Potential Problems
If grown in its native habitat and using a local seed stock, the smooth sumac should not be prone to debilitating pests or problems, Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) These materials are readily available from commercial plant sources, Contact your local Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Smooth Sumac., Look in the phone book under ”United States Government,” The Natural Resources Conservation Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture,”
Control
Please contact your local agricultural extension specialist or county weed specialist to learn what works best in your area and how to use it safely. Always read label and safety instructions for each control method. Trade names and control measures appear in this document only to provide specific information. USDA NRCS does not guarantee or warranty the products and control methods named, and other products may be equally effective.
Fact Sheet
Uses
Sumac serves primarily as a winter emergency food for wildlife. Ring-necked pheasant, bobwhite quail, wild turkey, and about 300 species of songbirds include sumac fruit in their diet. It is also known to be important only in the winter diets of ruffed grouse and the sharp-tailed grouse. Fox squirrels and cottontail rabbits eat the sumac bark. White-tail deer like the fruit and stems. Sumac also makes good ornamental plantings and hedges because of the brilliant red fall foliage. It is best used on drastically disturbed sites where pioneer species are desirable.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Weediness
This plant may become weedy or invasive in some regions or habitats and may displace desirable vegetation if not properly managed, Please consult with your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, or state natural resource or agriculture department regarding its status and use, Weed information is also available from the PLANTS Web site at plants,usda, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Smooth Sumac.,gov,
Description
Anacardiaceae Family. Smooth sumac is a U.S. native, deciduous, large shrub to small tree, seldom over 10-15 feet tall. It has alternate, compound leaves, 16-24 inches long. The leaflets are narrowed or rounded at the base and sharply pointed at the tip with finely toothed edges. The leaflets are dark green and smooth above, and pale beneath, except along the midrib. Compact clusters of greenish-yellow flowers bloom from June to July, and fruits mature from August to September. The fruiting head is a compact cluster of round, red, hairy fruits called drupes. Each drupe measures ¼ inch in diameter and contains one seed. Each cluster of drupes may contain 100 to 700 seeds. Fruit is produced on plants 3 to 4 years old. Because most populations of sumac have male and female flowers on separate plants, only the female plants produce seed. Occasionally, plants are found which have both male and female flowers. The germination of sumac seeds is enhanced by their passage through the digestive system of rabbits, ring-necked pheasants, and quail. The presence of fire also encourages increased germination. There are about 75,000 seeds per pound. Joseph Ruffner USDA NRCS National Plant Materials Center Beltsville, Maryland
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution
Distribution
Smooth sumac is widely distributed throughout the United States. It is extremely drought resistant and is commonly found in open fields and roadsides, fence rows, railroad rights-of-way, and burned areas, on sandy or gravelly soil. All sumacs are tolerant of slightly acid soil conditions and textures ranging from coarse to fine. Sumacs are not highly shade tolerate and are considered early successional species. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Establishment
One year old nursery grown seedlings are normally used for planting large areas. Once established, stands will spread from the root sprouts. The lateral root system is extensive and spread outward 3 or more feet a year. This sprouting is encouraged by cutting or fire injury. The colonies appear to lose vigor in about 15 years.
Management
Sumac stands can best be maintained by eliminating competing vegetation by mowing, chemicals, or fire. Sumacs fail to compete with invading tree species and are seldom found growing under a closed canopy. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) No known cultivars of this species are known to exist. Rooted plants may be available from specialty nurseries.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -33 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 135 |
| Hedge Tolerance | Low |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.3 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1200 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 300 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 24 |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Coppice Potential | Yes |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Short |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 12.0 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 12 |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Rhizomatous |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Seed per Pound | 59775 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Mid Spring |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |