Saltgrass
Scientific Name: Distichlis spicata (L.) Greene

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | DISP |
| Group | Monocot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Graminoid |
| Native Locations | DISP |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Inland saltgrass, seashore saltgrass, spike grass, and alkali grass , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Saltgrass.
Uses
Livestock: Under favorable soil and moisture conditions, studies have shown Saltgrass favorable for pastures irrigated with saline water. The total dry matter yields were 9081 kg/ha with a total protein production of 1300 kg/ha. Saltgrass is grazed by both cattle and horses and it has a forage value of fair to good because it remains green when most other grasses are dry during the drought periods and it is resistant to grazing and trampling. It is cropped both when green and in the dry state; however, it is most commonly used the winter for livestock feed. Saltgrass along the Atlantic coast was the primary source of hay for the early colonists. Wildlife: Saltgrass is a larval foodplant for the Wandering Skipper (Panoquina panoquinoides errans) butterfly. It is also an important food in the diet of waterfowl and the Florida salt marsh vole (Microtus pennsylvanicus dukecampbelli), which is on the Endangered and Threatened Species List of Southeastern United States. Ducks are reported to occasionally eat the dried seeds and controlled burning provides tender forages for wild geese. Distichlis spicata is significant in the salt marshes, which provide nesting grounds for birds, fish and larvae of many species of marine invertebrate animals. As salt marsh plants decompose, their stored nutrients provide a steady source of food for clams, crabs, and fish. Hitchcock (1950) Texas A&M University Wetland Restoration: The thick entangled roots of salt marsh plants acts as a guard between the ocean and the shore protecting the land from pollutants and other chemicals associated with runoff water. It is particularly useful in saline/alkaline wetlands. Medicine: Saltgrass is a respiratory allergenic plant that is offered by Miles Pharmaceutical and used by Florida physicians to treat respiratory allergies. Spice: Indians that inhabited California used saltgrass as a seasoning. They collected the salt crystals by threshing the blades. The seasoning provided is gray-green and said to have tasted like a salty dill pickle.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
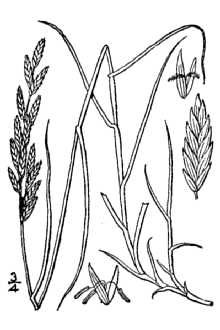
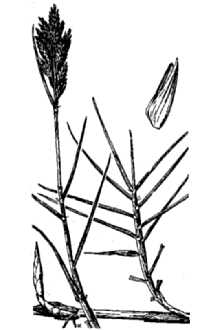
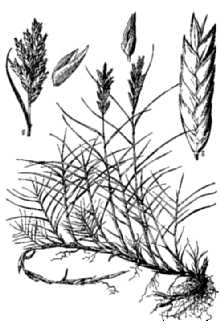
General: Grass Family (Poaceae). Inland saltgrass is a native, dioecious low, glabrous perennial, with scaly rhizomes. Culms are erect, varying in heights of 1.5 – 4.5 dm, less tall in dense colonies. Lower leaves consist of sheaths only, which are overlapping and glabrous. Sheath margins are scarious and sparsely ciliated apically. Leaves are mostly cauline and vertically two-ranked. Blades are firm, the edges often flat at the base and folded or rolled inward meeting in the middle, therefore, appearing attenuate. Blades are generally less than 10 cm long. Salt crystals may be found on the leaves and stems. The ligules are stiff, membranous and apically ciliate. Ligules range in lengths between 0.2-0.5 mm long. The inflorescences are dense, spike-like panicles, which range from 5-7 cm long or less. Spikelets are 3-10 flowered and are laterally flattened. Disarticulation is above the glumes and between the florets. The two glumes are unequal in size. Glumes are keeled and hard on the back. The margins of the glumes are scarious; the first glume is 1-3 nerved and 1.5-2.5 mm long. The second glume is 3-5 nerved and 2-3 mm long. The lemmas are rounded on the back and have 9-11 faint nerves. Lemmas are acute to cuspidate and 3-4 mm long. The lemma margins are scarious. Paleas are 2-nerved, 3-5 mm long, falcate, and are sharply keeled, the keel very finely hispid-ciliate. The palea margins are scarious and are in-rolled.
Distribution
For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Establishment
Adaptation: Saltgrass is found in saline areas, brackish marshes, and in salt flats along the coasts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, the Gulf of Mexico and the along the coast of South America. It inhabits upper/high marsh (irregularly flooded) areas, in which the water levels vary between 2 inches above the soil surface and 6 inches below the soil surface. It is also commonly present in the dry West, where it is one of the most drought-tolerant species. Saltgrass is located in both organic alkaline and in saline soils. It is found in planting zones 7,8,9,and 10. Distichlis spicata can be found in flower from June to October. The inflorescence is yellowish in color, turning straw brown as it dries. General: It may be propagated by seeds, which are produced many times in a growing season and are dispersed by wind and water. It is easier and more often propagated by its extensively creeping underground rhizomes. Rhizomes: Saltgrass can be established by seeds or by rhizome cuttings. If using rhizome cuttings, they must not dry out. They may be stored up to 28 days. It is recommended that the rhizomes be stored in a temperature range of 35-50° F and in 60-75% relative humidity. Rhizomes are can be planted any time of the year at a depth of 1-2 inches. However, rhizomes sprout better at 77-86° F. Seeds: Saltgrass seeds demand more than rhizomes to sprout. The seeds need moist soil, low alkalinity and high temperatures. Although many seeds are produced, only a small percentage of those seeds may germinate naturally.
Management
Saltgrass can be managed by burning between September 1 and February 1 biannually, when the water level exceeds the soil surface. Following burning, four inches of re-growth should be obtained before grazing is allowed. Water control systems may need to be installed to maintain correct water levels to avoid prolong inundation, which kills saltgrass. Cattle walkways are usually installed to make the forage more accessible.
Pests and Potential Problems
Saltgrass is the alternate host for the red rust (Puccinia aristidae, also known as Puccinia subnitens) that infects spinach. Although the red rust disease is difficult for shippers to detect, it grows rapidly during transit. Since little is known about this disease, there are no recommended control techniques. Saltgrass eradication has been the only method used so far because the pathogen cannot complete its life cycle without this alternate host plant.
Control
This species can behave invasively in some situations. Please contact your local agricultural extension specialist or county weed specialist to learn what works best in your area and how to use it safely. Always read label and safety instructions for each control method. Trade names and control measures appear in this document only to provide specific information. USDA, NRCS does not guarantee or warranty the products and control methods named, and other products may be equally effective. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) ‘LK517f saltgrass’ is a California native, perennial, warm season grass with extensive creeping, yellowish, scaly rhizomes forming large colonies. Establishment should be in late spring using rhizomes or plugs planted on one-foot centers. Irrigation water should be applied the first summer to ensure stand establishment. LK517f is used for riparian restoration and bank and shoreline stabilization. Contact your local Natural Resources
Conservation
Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources Conservation Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”
References
Ahlgren, G.H. 1956. Forage crops. McGraw Hill Book Company, Inc., New York, New York. 7 p. Allen, C.M. 1992. Grasses of Louisiana. 2nd ed. Cajun Prairie Habitat Preservation Society, Louisiana. 96 p. Austin, D.F. 1998. Respiratory allergenic plants. AUG00. http://www.fau.edu/divdept/science/envsci/allergy.html Bentley Community College 1997. Salt marshes. AUG00. http://web.bentley.edu/sum97/ns314/ecosystems/saltcomm.htm1 Comer, W.L. & D.G. Lugg 1983. Yield and quality of saltgrass (Distichlis spicata (L.) Greene) grown in two soils and several salinities. Western Society of Crop Science Abstracts. AUG99. http://ectc.ext.missouri.edu:70/R13180-14574-1m/info/wscs/abstracts/83.html The University of Arizona 1997. Arizona range grasses. College of Agriculture, Cooperative Extension. AUG99. http://phylogeny.arizona.edu/pubs/natresources/az97105/desert_ saltgrass.html Colorado State University 1996. Red rust on spinach. Cooperative Extension Pest Alert Bulletin, Vol. 13, No. 7 May 31, 1996. Red Rust on Spinach. AUG99. http://www.colostate.edu/Depts/IPM/news/pestalrt/Vol13/pest13-7.htm USDI, FWS 1992. Endangered and Threatened tpecies of southeastern United States (The Red Book) FWS Region – 4 As of 11/92. AUG99. http://www.fws.gov/r9endspp/i/a/saa98.html Godfrey, R. K. & J.W. Wooten 1979. Aquatic and wetland plants of Southeastern United States – Monocotyledons. University of Georgia Press, Athens, Georgia. 213 p. Gordon–Garrison, M. 1994. Gardening naturally. AUG00. http://sdcc12.ucsd.edu/~wa12/garden11.94.html Kim, J.G. & B. Grenwell 1999. UCD wetlands lab/wetland plants. AUG99. http://www.des.ucdavis.edu/wetlands/plants/ds.html Leithead, H.L., L.L. Yarlett, & T.N. Shiflet 1971. 100 native forage grasses in 11 southern states. USDA Handbook No. 389. 83 p. Oregon Coast.Com 1999. Neterts Bay: Oregon coast – salt marsh & mudflats. http://www.oregoncoast.com/Netarts/nbay3.htm Sampson, A.W. 1924. Native American forage plants. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, New York. 172 pp. Struttman, J. 1999. Butterflies of New Jersey. USDI, GS, BRD, Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center. AUG00. http://www.npwrc.usgs.gov/resource/distr/lepid/BFLYUSA/nj/5159.htm Szalay, F.A. & V.H. Resh 1996. Responses of wetland invertebrates and plants important in waterfowl diets to burning and mowing of emergent vegetation. Wetlands 17: (1996). AUG99. http://www.sws.org/wetlands/abstracts/volume17n1/SZALAY.html Uchytil, R.J. 1990. Distichlis spicata. IN: The fire effects information system [Database]. USDA, Forest Service, Intermountain Research Station, Intermountain Fire Sciences Laboratory, Missoula, Montana.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
Inland saltgrass, seashore saltgrass, spike grass and alkali grass.
Uses
Livestock: Under favorable soil and moisture conditions, studies have shown Saltgrass favorable for pastures irrigated with saline water. The total dry matter yields were 9081 kg/ha with a total protein production of 1300 kg/ha. Saltgrass is grazed by both cattle and horses and it has a forage value of fair to good because it remains green when most other grasses are dry during the drought periods and it is resistant to grazing and trampling. It is cropped both when green and in the dry state; however, it is most commonly used the winter for livestock feed. Saltgrass along the Atlantic coast was the primary source of hay for the early colonists.
Wildlife
Distichlis spicata is significant in the salt marshes, which provide nesting grounds for birds, fish and larvae of many species of marine invertebrate animals. As salt marsh plants decompose, their stored nutrients provide a steady source of food for clams, crabs, and fish. : Saltgrass is a larval foodplant for the Wandering Skipper (Panoquina panoquinoides errans) butterfly. It is also an important food in the diet of waterfowl and the Florida salt marsh vole (Microtus pennsylvanicus dukecampbelli), which is on the Endangered and Threatened Species List of Southeastern United States. Ducks are reported to occasionally eat the dried seeds and controlled burning provides tender forages for wild geese. Wetland Restoration: The thick entangled roots of salt marsh plants acts as a guard between the ocean and the shore protecting the land from pollutants and other chemicals associated with runoff water. It is particularly useful in saline/alkaline wetlands. Medicine: Saltgrass is a respiratory allergenic plant that is offered by Miles Pharmaceutical and used by Florida physicians to treat respiratory allergies. Spice: Indians that inhabited California used saltgrass as a seasoning. They collected the salt crystals by threshing the blades. The seasoning provided is gray-green and said to have tasted like a salty dill pickle.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e,g, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Saltgrass., threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values),
Description
Saltgrass is a native perennial from 15” to 35” in height. It forms dense mats with rhizomes and sometimes stolons. It is a dioecious species with male and female reproductive parts on separate plants. It is widespread and in the eastern United States is most commonly found along estuaries and the troughs of back dune areas along the shorelines. Distribution: Please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Establishment
Adaptation: Saltgrass is found in saline areas, brackish marshes, and in salt flats along the coasts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, the Gulf of Mexico and the along the coast of South America. It inhabits upper/high marsh (irregularly flooded) areas, in which the water levels vary between 2 inches above the soil surface and 6 inches below the soil surface. It is also commonly present in the dry West, where it is one of the most drought-tolerant species. Saltgrass is located in both organic alkaline and in saline soils. It is found in planting zones 7,8,9,and 10. Distichlis spicata can be found in flower from June to October. The inflorescence is yellowish in color, turning straw brown as it dries. General: It may be propagated by seeds, which are produced many times in a growing season and are dispersed by wind and water. It is easier and more often propagated by its extensively creeping underground rhizomes. Rhizomes: Saltgrass can be established by seeds or by rhizome cuttings. If using rhizome cuttings, they must not dry out. They may be stored up to 28 days. It is recommended that the rhizomes be stored in a temperature range of 35-50° F and in 60-75% relative humidity. Rhizomes are can be planted any time of the year at a depth of 1-2 inches. However, rhizomes sprout better at 77-86° F. Seeds: Saltgrass seeds demand more than rhizomes to sprout. The seeds need moist soil, low alkalinity and high temperatures. Although many seeds are produced, only a small percentage of those seeds may germinate naturally.
Management
Saltgrass can be managed by burning between September 1 and February 1 biannually, when the water level exceeds the soil surface. Following burning, four inches of re-growth should be obtained before grazing is allowed. Water control systems may need to be installed to maintain correct water levels to avoid prolong inundation, which kills saltgrass. Cattle walkways are usually installed to make the forage more accessible.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -35 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 80 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 10.0 |
| pH, Minimum | 6.4 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 43000 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 11000 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 70 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 5 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 2 |
| Salinity Tolerance | High |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Slow |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Semi-Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring, Summer, Fall |
| Bloat | None |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | Yes |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 1.1 |
| Growth Rate | Slow |
| Growth Form | Rhizomatous |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Low |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Seed per Pound | 519000 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | Yes |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Low |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Mid Summer |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |