Red Spruce
Scientific Name: Picea rubens Sarg.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | PIRU |
| Group | Gymnosperm |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Tree |
| Native Locations | PIRU |
Plant Guide
Use a soil moisture meter to monitor the soil moisture where Red Spruce is planted.
Fact Sheet
Uses
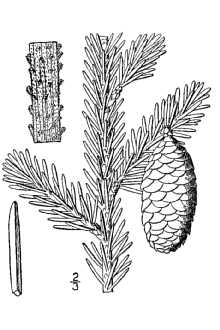
Red spruce is one of the most important forest trees in the northeast. The wood is light, soft, narrow-ringed and faintly tinged with red. It is the most common species of eastern spruce lumber. Because of its resonance, it is especially adapted to sounding boards in musical instruments. It makes up a large percentage of spruce pulpwood produced in the northeast. It is used as a Christmas tree also. Red spruce provides food and cover for various mammals and birds. The spruce grouse feeds on the buds and foliage; red squirrels eat buds and seeds; varying hare browse twigs and foliage; porcupines feed upon the bark. Red spruce seeds make up 25 to 50 percent of the diet of white-winged crossbills. Red spruce can be an important cover tree in northern New England deer yards.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
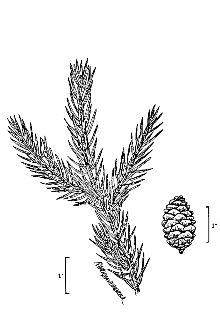
Red spruce reaches heights of 60 to 80 feet with trunk diameters of nearly two feet. Larger sizes are attained in the southern Appalachians. Needles are four sided, dark, shiny, yellow-green, and about 1/2 inch long, growing singly from all sides of the twigs and branches. The slender new twigs have a reddish coat of down through the first year. This, together with the short incurved needles, help distinguish red spruce from most other spruces. There are about 139,000 seeds per pound.
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution
Distribution
In northern New England it is found mainly on shallow till soils that average about 18 inches deep to a compact layer. At higher elevations it often grows in organic soils overlying rocks. On poorly drained soils, lack of aeration limits its growth. In the northern part of its range, red spruce grows at elevations from near sea level to about 4,500 feet. In the southern Appalachians it is limited to slopes and mountain tops above 3,500 feet in West Virginia and above 4,500 feet in Tennessee and North Carolina. Robert H. Mohlenbrock USDA NRCS 1995 Northeast Wetland Flora @ USDA NRCS PLANTS Unfortunately, red spruce is showing damage from air pollution throughout its range, particularly at the higher elevations. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website.
Establishment
Good seed production of red spruce usually begins after the tree is 30 years old, Heavy seed crops occur every three to eight years, Spruce seedlings have exceptionally slow growing, fibrous, shallow roots, Consequently, a critical survival factor in natural establishment is the depth of the organic layers on which the seed germinates, If the thickness of the layer exceeds two inches, the roots of spruce seedlings may not reach mineral soil and the moisture needed to carry them through dry periods, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Red Spruce., Red spruce is very shade tolerant, but requires nearly full sun light for optimum development, Red spruce can be established in nurseries as easily as any of the other spruces, It is used some for reforestation in the northeast,
Management
Red spruce has not generally received intensive management in the northeast. It can be harvested by partial cutting or clear cutting depending upon local markets and silvicultural conditions. Weeding and releasing, if needed, should be done at an early age, 10 to 15 years.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -47 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | None |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 90 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 5.8 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.0 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 700 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 300 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 52 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 28 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 13 |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Tolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Conical |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Dense |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Leaf Retention | Yes |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 110.0 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 25 |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Single Stem |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Seed per Pound | 140000 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Mid Spring |
| Propagated by Cuttings | Yes |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | Yes |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | Yes |
| Post Product | Yes |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | Yes |
| Lumber Product | Yes |
| Fuelwood Product | Medium |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |