Common Carpetgrass
Scientific Name: Axonopus fissifolius (Raddi) Kuhlm.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | AXFI |
| Group | Monocot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Graminoid |
| Native Locations | AXFI |
Plant Guide
Use a soil moisture meter to monitor the soil moisture where Common Carpetgrass is planted.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
Axonopus affinis, axonopus, caratao grass, carpet grass, teppichrasengras, grama-missioneira, gramalote zacate amargo, Louisiana grass, mat grass, narrowleaved carpetgrass
Uses
Common carpetgrass is grazed all year by livestock, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Common Carpetgrass., It is a managed pasture grass in some localities, It is also used on recreational areas such as campgrounds, parking lots, baseball fields, and picnic areas,
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status, such as, state noxious status and wetland indicator values.
Description
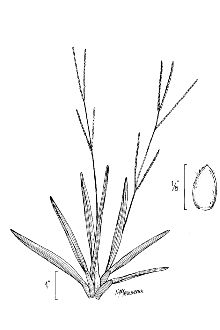
Grass Family (Poaceae). Common carpetgrass is a native, warm-season, stoloniferous perennial grass. The height is between 8 and 20 inches. The leaf blade is usually flat or folded; 1/4 to 1/2 inch wide; fine hair along margin near base; rounded or slightly pointed; and reddish or purplish near maturity. The ligule is a minute membrane. The seedhead is usually 3 slender racemes 1-1/2 to 4 inches long, 2 at summit and 1, rarely 2, below. Distribution: For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Management
For maximum production and most efficient harvest by livestock, grazing should be rotated about every 30 to 40 days and no more than 50 percent of current year's growth by weight grazed off. A 2- to 3-inch stubble height is a good gage of proper use. Fertilization is not profitable on all sites.
Establishment
In southern Florida, common carpetgrass stays green all year. Elsewhere, it becomes dormant early in the fall and starts growth in the spring. It produces seedheads and stolons during the active growth period. It reproduces from stolons and from seed. Pure stands are common. It is adapted to clays, sands, mucks, and peats. Most commonly, it is found on slightly acid sandy to sandy loam soils that have a favorable soil-moisture relationship. Cultivars, Improved and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Please contact your local NRCS Field Office.