Antelope Bitterbrush
Scientific Name: Purshia tridentata (Pursh) DC.
| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | PUTR2 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Shrub |
| Native Locations | PUTR2 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Antelopebrush, buckbrush, quininebrush, bitterbrush, antelope-brush, quinine brush, deer-brush, black sage
Uses
Antelope bitterbrush is one of the most important palatable native shrubs in the western United States. It provides high quality, important spring and winter browse for domestic livestock, antelope, deer, and elk. Its seed is an important source of food for small animals and the plant provides cover for small animals and birds. It is considered medium quality coverage for sage-grouse. The shrub is also used for reclamation and erosion control of mined areas and has the potential for use as a living snow fence, roadside beautification, and xeriscape plantings. Historic Native American Uses: Western Indian groups used leaf poultice or wash for itches, rashes, insect bites, chickenpox, and measles. Leaf tea was used as a general tonic and for colds, pneumonia, liver disease, to expel worms, and as an emetic and laxative for stomach ache and constipation. Twigs, leaves, and berries were used as a laxative. Root teas were used for coughs, lung and bronchial infections, fever, and to facilitate delivery of placenta.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
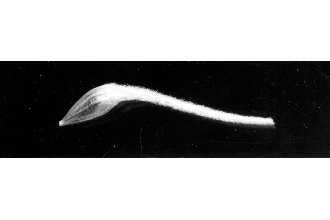
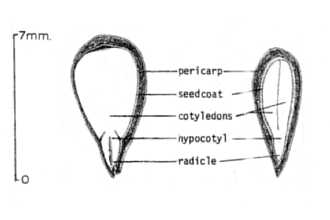
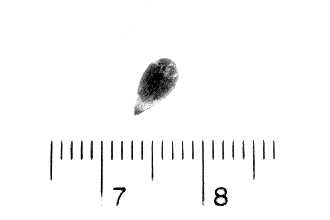
General: Antelope bitterbrush is a slow growing shrub that is moderate to very deep rooted with wide ecotypic variations. It is normally 2 to 6 feet in height and up to 8 feet in width with wedge shaped, three lobed leaves (some are persistent in winter). Leaves can vary in color from grey green to bright green. Some plants have branches near the soil that layer (branches that touch the soil develop roots) providing additional rooting for the plant. Flowering occurs in late spring to early summer. The spindle-shaped seed shatters easily at maturity. Flowers are small, varying from white to yellow, and produced profusely along each leader. The seeds are large for the species—15,500 per pound. They are about one-fourth inch long and obovate. Seeds, stems, and leaves are nontoxic. Individual bitterbrush plants exhibit considerable variation for growth form. Bitterbrush’s growth forms vary from a uniform, erect growth habit to more decumbent, layering forms. Users are encouraged to consider the various forms of bitterbrush in choosing a strain best suited to their needs. Distribution: Antelope bitterbrush is an important native browse shrub in the intermountain Western United States. It occurs from New Mexico north to Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, and British Columbia, west to Idaho, and Washington, south to Oregon, California, and Nevada. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Antelope bitterbrush occurs most often as part of a mixed shrub community, but occasionally is found in nearly pure stands. It is associated with a variety of understory grasses and forbs. It can also be an understory plant in association with taller growing trees.
Adaptation
Antelope bitterbrush is adapted to a wide range of soils with 8 to 34 inches of annual precipitation. It is normally found at elevations of 4000 to 8500 feet, but has been noted at 11,000 feet in California. The shrub has good tolerance to drought and cold. In California, bitterbrush is associated with big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) and rabbitbrush (Chrysothamnus sp.). It occurs naturally on dry lake beds, alluvial fans or terraces, and low foothills. It occurs in soils that are deep, gravelly, loamy coarse sands derived from granite, with pH ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. Tests have shown that bitterbrush has high potential for use on deep, coarse, well-drained, neutral to slightly acidic soils in areas that have 12-24 inches of annual precipitation.
Establishment
Natural establishment of antelope bitterbrush occurs in years with good seed production when rodents cache seed and do not use all of the caches. Moisture is necessary the first few years of seedling growth for establishment. Late fall or winter seeding is recommended and competition can be a problem for establishment. Seeds should be drilled about 1 inch deep at a rate of 1/2 to 2 (3) pounds per acre. Rates are doubled if broadcasting and seeds do need to be covered. In California, pretreatment with hydrogen peroxide is required to break dormancy for spring seeding and seedlings are susceptible to late frosts. Bitterbrush seedlings are often transplanted on critical sites. In such castes, moisture must be adequate to ensure survival in the first year. One-year-old bare-root or containerized seedling stock, 6 to 24 inches tall, is recommended. Plants should not be used for the first four years and seedlings need protection until they are 8 to 10 inches tall. Rodents normally cache seeds within 50 to 75 feet of an existing seed source. Suitable environmental conditions may allow natural revegetation in only one out of 20 years. Antelope bitterbrush can also be established with tubling plants. These should be planted in the spring or early summer. Establishment can be slow; however, stands tend to be long-lived. Several insects and diseases are known to damage the foliage, seed, and seedlings of bitterbrush, and are more or less susceptible than other species. High-density populations of grasshoppers can destroy seedlings.
Management
Since antelope bitterbrush is a very palatable shrub for big game and livestock, its use should be controlled or it can be easily eliminated by overuse. The shrub is most often used by big game in the fall, winter, or early spring when other plants are still covered by snow. Livestock tend to use the shrub during the growing season when use is more detrimental to vigor. Stands of bitterbrush can become decadent with no use and mature plants should be browsed for good forage production and vigor. However, no more that 50 to 60 percent of current annual growth should be removed. The literature indicates that bitterbrush is not a fire resistant shrub, but is fire dependent and light to moderate fires may enhance stands.
Pests and Potential Problems
Many species of insects and mites inhabit antelope bitterbrush, several of these are beneficial. It should be noted that bitterbrush is insect pollinated. Insects that cause problems include defoliators such as mountain mahogany loper and Western tussock moth. Some of the noted seed insects are bitterbrush seed midge, Say’s stinkbug, dark bitterbrush leaf tier, and flower thrips. Large numbers of seedlings and small plants have been destroyed by cutworms and false wireworms. Diseases associated with bitterbrush include root rot, root and stem wilt, and root-stem canker. Seedlings have been damaged by damping off (a disease caused by fungi). A beneficial organism associated with antelope bitterbrush is the nitrogen-fixing endophyte Frankia purshiae.
Environmental Concerns
Concerns
Concerns
There are no known environmental concerns associated with antelope bitterbrush.
Seeds and Plant Production
Plant Production
Plant Production
In Colorado, seed may not be produced in wildland stands for 8 to 20 years depending on existing conditions. Browsing should be reduced to 30 percent or less to obtain good seed production. Seed may not be produced from mature plants when stressed from drought or late freezes. Seed can be collected by hand by shaking branches and allowing the seed to fall in hand held collectors. Seeds vary in size from 15,000 to 33,000 per pound and germination normally ranges from 85 to 95 percent. A cold moist stratification period of up to six weeks may be required to obtain good germination. Tublings can be grown in a greenhouse for planting in a period of six months to one year. In California, mature seed must be harvested with 3 to 10 days of ripening because it shatters quickly after reaching maturity. Seed may be harvested into canvas hoppers or aluminum seed collection trays positioned under the shrubs prior to seed fall. Seed collection and orchard maintenance are simplified by the upright growth form. A 3.6 to 3.6 m to 4.9 x 4.9 m (12 x12 ft to 16 x 16 ft) spacing is recommended for antelope bitterbrush seed orchards. Plants in wildland stands reach full seed production in 8 to 20 years. With appropriate cultural practices, this period may be reduced to about 5 years for seed orchards. Nine-year old shrubs grown at 2.4 m (8 ft) spacings without irrigation or other cultural treatments at the Boise Shrub Garden, produced 118 g (0.26 lbs) of seed per shrub or 199 kg/ha (177 lbs/acre). Seed is easily cleaned to a purity of 95 percent using a two-screen fanning mill and a barley debearder. Shriveled black seed is nonviable and should be separated with the chaff. Seeds of bitterbrush are relatively large, averaging 34,507 seeds/kg (15,685 seeds/lb) for cleaned seed, with germination averaging about 84 percent. Seeds of bitterbrush remain viable for 15 years or more in open storage. On rangeland sites antelope bitterbrush is normally seeded in late fall or winter to permit field stratification of the seed. Pretreatment with hydrogen peroxide is required to break dormancy for spring seeding. Seedlings are susceptible to late frosts. Plants develop very slowly and must be protected from competition during the first two seasons. Recommended seeding rates are 1.2 to 3.3 kg/ha (1 to 3 lbs/acre). Bitterbrush may be established on critical sites by transplanting. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) ‘Lassen’ is a cultivar of antelope bitterbrush released in 1984 by USDA Forest Service, Shrub Sciences Laboratory, Provo, Utah, Soil Conservation Service, and Utah Division of Wildlife Resources, Ephraim Utah. Seven other agencies in California, Idaho, Nevada, and Oregon cooperated. Its origin is near Janesville in Lassen County, California. Fountain Green germplasm is a source identified release of antelope bitterbrush. It was released in 1990 by the USDA Forest Service, Shrub Sciences Laboratory, Provo, Utah, and the Utah Division of Wildlife Resources, Ephraim, Utah. Its origin is North of Fountain Green, Utah. Maybell germplasm was released in 1997 as a selected class release by Upper Colorado Environmental Plant Center. Five other agencies participated in the release. Maybell’s origin is Moffat County in Northwest Colorado, near the town of Maybell.
References
Block, Neil D, Purshia tridentata http://www,usask,ca/agriculture/plantsci/classes/range/purshia,html, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Antelope Bitterbrush., Accessed: May 2005, Foster, Steven and Christopher Hobbs, 2002, Western medicinal plants and herbs, Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, New York, 296-7 p, Giunta, Bruce C,, Richard Stevens, Kent R, Jorgensen, and A, Perry Plummer 1978, Antelope Bitterbrush – An Important Wildland Shrub, Utah State Div, of Wildlife Resources, 48 pp, Plummer, A, Perry 1968, Restoring big –game
Range
in Utah. Utah Div. of Fish and Game. 183 pp. Shaw, Nancy and Stephen B. Monsen. No date. Notice of release of ‘Lassen’ antelope bitterbrush. USDA NRCS. Wasser, Clinton H. 1982. Ecology and culture of selected species useful in revegetating disturbed lands in the West. U.S. Dept. Int., Fish Wildl. Serv. FWS/OBS-82/56. 347 pp. USDA NRCS. September 1986. ‘Lassen Antelope Bitterbrush’ brochure. Davis, California USDA- Soil Conservation Service 1991.
Conservation
tree and shrub cultivars in the United States. Ag. Handbook 692. U.S. Govt. Printing Office.50 pp. Release information for ‘Lassen’ and Maybell Select Class.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
Antelopebrush, buckbrush, quininebrush
Uses
Antelope bitterbrush is a very palatable, high quality shrub for big game and livestock. It also provides cover for small animals and birds. It is considered a medium quality cover for sage-grouse. Bitterbrush seed is an important source of food for small animals. The shrub is also used for reclamation of mined areas where adapted. It has the potential for use as a living snow fence, roadside beautification, and xeriscape plantings.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your state Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description and Adaptation
Adaptation
Adaptation
Antelope bitterbrush is an important native browse shrub in the intermountain Western United States. It is adapted to a wide range of soils with 8 to 34 inches of annual precipitation and occurs at elevations of 4000 to 8500 feet, but has been noted at 11,000 feet in California. The shrub is slow growing with a moderate to very deep root system and wide ecotypic variations. It is normally 2 to 6 feet in height and up to 8 feet in width with wedge shaped, three lobed leaves (some are persistent in winter). Branches near the soil may layer (branches that touch the soil develop roots) providing additional rooting for the plant. Flowering occurs in late spring to early summer with yellow to white blossoms.
Establishment
Natural establishment of antelope bitterbrush occurs in years with good seed production when rodents cache seed and do not use all of the caches. Moisture is necessary the first few years of seedling growth for establishment. Late fall or winter seeding is recommended and competition can be a problem for establishment. Plants should not be used for the first four years and seedlings should be protected until they are 8 to 10 inches tall. Rodents normally cache seeds within 50 to 75 feet of an existing seed source. Suitable environmental conditions may allow natural revegetation in only one out of 20 years. Antelope bitterbrush can also be established with tubling plants. These should be planted in the spring or early summer.
Management
Since antelope bitterbrush is a very palatable shrub for big game and livestock, its use should be controlled or it can be easily eliminated by over use, The shrub is most often used by big game in the fall, winter, or early spring when other plants are still covered by snow, Stands of bitterbrush can become decadent with no use and mature plants should be browsed for good forage production and vigor, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Antelope Bitterbrush., However, no more than 50 to 60 percent of current annual growth should be removed, The literature indicates that bitterbrush is not a fire resistant shrub, but is fire dependent and light to moderate fires may enhance stands,
Pests and Potential Problems
Many species of insects and mites inhabit antelope bitterbrush, several of these are beneficial. It should be noted that bitterbrush is insect pollinated. Insects that cause problems include defoliators such as mountain mahogany loper and Western tussock moth. Some of the noted seed insects are bitterbrush seed midge, Say’s stinkbug, dark bitterbrush leaf tier, white collared leaf tier, and flower thrips. Large numbers of seedlings and small plants have been destroyed by cutworms and false wireworms. Diseases associated with bitterbrush include root rot, root and stem wilt, and root-stem canker. Seedlings have been damaged by damping off (a disease caused by fungi).
Environmental Concerns
There are no known environmental concerns associated with antelope bitterbrush. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) ‘Lassen’ is a cultivar of antelope bitterbrush released in 1984 by USDA Forest Service, Shrub Sciences Laboratory, Provo, Utah, Soil Conservation Service and Utah Division of Wildlife Resources, Ephraim, Utah. Seven other agencies in California, Idaho, Nevada, and Oregon cooperated. Its origin is near Janesville in Lassen County, California. Fountain Green germplasm is a source identified release of antelope bitterbrush. It was released in 1990 by the USDA Forest Service, Shrub Sciences Laboratory, Provo, Utah, and the Utah Division of Wildlife Resources, Ephraim, Utah. Its origin is North of Fountain Green, Utah. Maybell germplasm was released in 1997 as a selected class release by Upper Colorado Environmental Plant Center. Five other agencies participated in the release. Maybell’s origin is Moffat County in Northwest Colorado, near the town of Maybell.
Prepared By and Species Coordinator
Species Coordinator
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Fire Tolerance | None |
|---|---|
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | None |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Fire Tolerance | None |
| Fire Tolerance | None |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 100 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 100 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 120 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 140 |
| Hedge Tolerance | Low |
| Hedge Tolerance | Low |
| Hedge Tolerance | Medium |
| Hedge Tolerance | Medium |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -43 |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 20 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 24 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 10 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 12 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 12 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 8 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 20 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 20 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 20 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 20 |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Intermediate |
| Shade Tolerance | Intermediate |
| Shade Tolerance | Intermediate |
| Shade Tolerance | Intermediate |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -28 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -33 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -36 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 20 |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.6 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.6 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.6 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1200 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 20 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 390 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 300 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 1212 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 1200 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 2728 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1800 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1200 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.6 |
Morphology/Physiology
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Shape and Orientation | Semi-Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Flower Color | White |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Blue |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | Low |
| Nitrogen Fixation | Low |
| Nitrogen Fixation | Low |
| Nitrogen Fixation | Low |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 6.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 6.0 |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Blue |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Blue |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 6.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 3.0 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 6 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 6 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 6 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 3 |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
Reproduction
| Seed per Pound | 17193 |
|---|---|
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed per Pound | 17193 |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed per Pound | 17193 |
| Seed per Pound | 17193 |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Spring |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Early Spring |
| Bloom Period | Early Spring |
| Bloom Period | Early Spring |
| Bloom Period | Early Spring |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
Suitability/Use
| Post Product | No |
|---|---|
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Post Product | No |
| Protein Potential | High |
| Protein Potential | High |
| Protein Potential | High |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |