Alkali Sacaton
Scientific Name: Sporobolus airoides (Torr.) Torr.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | SPAI |
| Group | Monocot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Graminoid |
| Native Locations | SPAI |
Plant Guide
Alternative Names
giant sacaton, finetop saltgrass, hairgrass dropseed, zacaton alcalino
Uses
Ethnobotanic: The Hopi Indians use the seeds in times of famine (Whiting 1939). They were ground into flour, eaten dry or made into a mush. Wildlife: Alkali sacaton’s abundant herbage is eaten by cattle, sheep, and horses (Hitchock 1951). This species is used as a good forage or grazing grass in lowland and in alkali regions (Gates 1937).
Status
Please consult the Plants Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status, such as, state noxious status and wetland indicator values.
Description
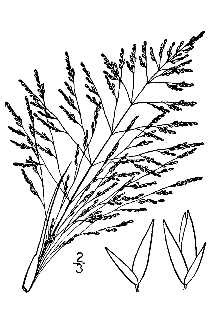
General: Grass Family (Poaceae). Alkali sacaton is a tough perennial two to three and a half feet tall, growing in large bunches. The culms are erect to spreading and range in height from 50 to 100 centimeters tall. The blades are elongate, flat, soon becoming involute, and usually less that four millimeters wide (Hitchcock 1951). Distribution: Alkali sacaton ranges from South Dakota to Washington, south to Missouri, Kansas, Texas, and Mexico (Steyermark 1963). For current distribution, please consult the Plant profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. R. Mohlenbrock USDA,NRCS,Wetland Sciences Institute @PLANTS
Adaptation
Alkali sacaton grows on dry to moist sites with sand or gravelly soil. This species is often found growing on alkaline flats, prairies, and sandy plateaus. It is common along drainage in desert and semi-desert areas.
Establishment
Propagation by Seed: Alkali sacaton seeds should be sown in the spring in a greenhouse. Cover the seeds with a light layer of the growing media. Germination for this species should take place within two weeks. When seedlings are large enough to handle, plant them directly into their permanent positions in the summer. Large divisions can be planted directly into their permanent positions. However, smaller divisions should be placed in individual pots in a cold frame, planting them when they are well established in the summer.
Management
Once Sporobolus airoides plants are well established little maintenance is required, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Alkali Sacaton., It is best that the stands of this species is grazed in the spring and summer when growth is active, Cultivars, Improved and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Commonly available through commercial seed vendors, Contact your local Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil
Conservation
Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources Conservation Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”
References
Britton, N.L. & A. Brown 1970. An illustrated flora of the northern United States and Canada. Dover Publications, New York, New York. Gates, F.C. 1937. Grasses in Kansas. Kansas State Printing Plant, Topeka, Kansas. Hitchcock, A.S. 1951. Manual of the grasses of the United States. Misc. Publ. No. 200. U.S. Department of Agricultural, Washington, D.C. Hitchcock, A.S. 1971. Manual of the grasses of the United States. Dover Publications, New York, New York. Kearney, T.H.; R.H. Peebles; J. T. Howell; & E. McClintock 1960. Arizona flora. 2nd ed. University of California press, Berkeley, California. Munz, P.A. 1974. A flora of southern California. University of California Press, Berkeley, California. Steyermark, J.A. 1963. Flora of Missouri. The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa. The Great Plains Flora Association 1986. Flora of the Great Plains. University Press of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas. Whiting, A.F. 1939. Ethnobotany of the Hopi. North Arizona Society of Science and Art.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
bunchgrass, finetop salt grass
Uses
Livestock: Alkali sacaton is good forage for horses and cattle in the far western United States in arid or semiarid regions. Wildlife: This plant is a source of food for deer, small mammals (it is relished by jackrabbits), birds (game and non game), and waterfowl. Conservation: Alkali sacaton is frequently utilized for seeding and stabilizing disturbed areas. Due to its salt tolerance, it is recommended for seeding saline sites such as oil well pits and saline waste from power generating plants. Landscaping: A mass planting of this species could create a contrast to coarser foliaged plants.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description and Adaptation
Adaptation , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Alkali Sacaton.
Adaptation
Alkali sacaton is a native perennial large bunchgrass ranging in height from 50 to 150 cm (20-60 inches). The leaves are flat, 2-6 mm (1/16-1/4 inches) wide, and taper from the base of the leaf. The inflorescence is an open panicle 20-50 cm (8-20 inches) long with a pyramidal shape. The small seeds rest singly on branches in the loose, open seedhead. Bloom periods vary by region: April to May in the Southwest, June-October in the Great Plains, and July-August in the Northwest. Alkali sacaton is found in the western half of the United States. It grows in both saline and nonsaline coarse, medium, and fine textured soils. This grass is tolerant of salinity and a broad range of pH. After establishment, alkali sacaton is tolerant of drought and water inundation. However, it is intolerant of shade and is found growing in open areas.
Establishment
Alkali sacaton reproduces from seeds and tillers. The seeds remain viable for years and germinate without being scarified. In Utah, a seed study reported 99% seed germination of seeds that were stored in an open warehouse for 7 years. Plant seeds in the spring when soil temperature will be near 86 0 F (30 0 C) and precipitation probabilities are greatest. The plants can survive on 12 to 18 inches of precipitation per year.
Management
Alkali sacaton is an important forage species in the arid and semiarid regions of the Southwest United States. The grass is tolerant of moderate grazing and a good forage producer. It has the ability to efficiently use extra water during forage production. Alkali sacaton is tolerant of fire; however, it can be killed if the fire is severe. Fire recovery has been reported from 2 to 4 years. Summer fires have more of an effect than winter fires.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
|---|---|
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 180 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 150 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 136 |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -38 |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -23 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -13 |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Salinity Tolerance | High |
| Salinity Tolerance | High |
| Salinity Tolerance | High |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 5 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 5 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 5 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 13 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| pH, Maximum | 9.0 |
| pH, Maximum | 9.0 |
| pH, Maximum | 9.0 |
| pH, Minimum | 6.6 |
| pH, Minimum | 6.6 |
| pH, Minimum | 6.6 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 13 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 13 |
Morphology/Physiology
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Bloat | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 3.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 3.0 |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 3.0 |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
Reproduction
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
|---|---|
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Seed per Pound | 1750000 |
| Seed per Pound | 1750000 |
| Seed per Pound | 1750000 |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seedling Vigor | Low |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Bloom Period | Mid Summer |
| Bloom Period | Mid Summer |
| Bloom Period | Mid Summer |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
Suitability/Use
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
|---|---|
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |