Trifolium hybridum L. var. pratense Rabenh.
Scientific Name: Trifolium hybridum L. var. pratense Rabenh.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | TRHYP8 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | AnnualPerennial, |
| Growth Habits | Forb/herb |
| Native Locations | TRHYP8 |
Plant Guide
Uses
Alsike clover is used for hay, pasture, and soil improvement, and is preferred where very wet or acid soils are encountered. It is generally out produced by other clover species for particular uses. Alsike clover is seldom grown by itself as it grows well in mixtures with grasses. Grass/alsike clover mixtures are easier to harvest for hay because the grass holds the clover more upright. Normally only one cutting can be harvested for hay in a season. Many wildlife species use legumes and are attracted to the early green up to help them recover from the stress of winter. Alsike clover is not particularly noted for providing wildlife cover or food. The flowers are especially attractive to bees, especially honey bees for the nectar and pollen.
Status
Consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Weediness
Alsike clover may become weedy or invasive in some regions or habitats and may displace desirable vegetation if not properly managed. Consult your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, or state natural resource or agriculture department regarding its status and use. Weed information is also available from the PLANTS Web site at plants.usda.gov.
Description
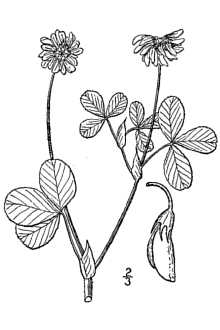
Alsike clover is a true species in spite of its specific name which originally implied that it was a hybrid of red clover (T. pretense) and white clover (T. repens). It is an introduced, short-lived, non-creeping perennial with a growth habit similar to red clover. It can be distinguished from red clover by the absence of crescent-shaped marks on each leaflet and more conspicuously toothed leaves. Tillers grow profusely from the crown. Leaves are glabrous (smooth) and stipules are long with a tapering point. Stems are semi-erect, long, thin, smooth and usually hollow with very short, almost spherical axillary racemes about 2-3.5 cm (0.75-1.4 inches) in diameter. Each raceme has about 30-50 white or pale pink flowers. Individual flowers are about 6-11mm long. Flowers bend downwards after pollination and turn brown at maturity. Each seed pod is about 1 cm (0.4 inches) long and contains 3-5 seeds and vary in color from dull green to nearly black. Alsike clover has a branched tap root. Small lateral outgrowths (nodules) are usually present on the root. Alsike clover reaches a height of 2-4 feet. This introduced plant tends to recline or lodge unless companion plants help hold the stem upright. USDA NRCS National Plant Materials Center Beltsville, MD
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Trifolium hybridum L. var. pratense Rabenh..
Distribution
Alsike clover is adapted to a wide range of soil types and grows well in northern latitudes and at high elevations. It survives severe winters and performs best where summers are cool. It grows well on soils that are too acidic for red clover (pH < 6.0) and can tolerate more alkalinity than most clovers. It will tolerate wetter soils better than other clovers. It prefers silty clay loams where moisture is sufficient throughout the growing season (mean annual precipitation 18 inches or more) or can be supplied by irrigation. Alsike clover does not tolerate droughty sites but will tolerate soils that are completely waterlogged and will withstand spring flooding up to 6 weeks. It is not shade tolerant. Cultivars of alsike clover are either diploid (2n = 16) or tetraploid (2n = 36). The cultivars used in North America are diploid. Most European cultivars are tetraploid and are taller, have larger leaves and flowers and are later maturing. Alsike clover is distributed throughout the United States. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website. Alsike clover is believed to have originated from near the village of Alsike in central Sweden. It has been grown extensively in Europe since the early 1800’s and was introduced to North America around 1840.
Establishment
Alsike clover has approximately 680,000 seeds per pound. The full seeding rate is 3 pounds PLS per acre for a solid stand. The recommended rate for a grass/legume pasture is 25% or 0.75 pounds PLS per acre. For pasture establishment, seed is drilled into a well-prepared seedbed that has been plowed, harrowed, and compacted to produce a very firm seedbed. The seed should be inoculated with the correct Rhizobium before seeding. Seeding depth should be 1/8- 1/4 inch. Typically in grass/legume mixtures, the grass is drill seeded in rows and alsike clover is over seeded to limit competition from grass. For stabilization use, seed is often broadcast by cyclone seeders, hydroseeders, or blower-type equipment. The proper time of seeding is determined by seasonal moisture conditions. In most areas, this may vary from early April to mid May. Late summer and fall seedings should only be conducted when the site is irrigated and when at least six weeks of growing season remain to assure establishment before freezing conditions.
Management
Alsike clover is usually planted with grasses for pasture and hay in areas where other higher yielding legumes are not adapted. Pure stands of alsike clover should be harvested for hay when in full bloom. However, there may be many heads with ripe seed when a field is in full bloom. Despite the presence of some mature heads, the fine stems of alsike clover keep growing and do not harden quickly. This will allow for harvesting nutritious hay over an extended time but it should not be allowed to become too ripe. The presence of ripe seed in hay that is cut too late often causes slobbering in horses. Straw from seed production or late cutting hay makes fair winter feed for sheep, foals and young cattle. A mixture of alsike and red clover makes good hay. Although alsike clover is lower yielding than red clover, it withstands excessive soil moisture and is more tolerant of acid soils. Mixtures of alsike and red clover ensure some clover is present if the red clover fails to establish on water-logged and/or low pH areas within a field. Alsike and red clover mixtures will produce more hay combined than when planted separately. Alsike clover is most commonly used in a mixture with timothy but is also compatible with brome grasses. Avoid planting alsike clover with tall-statured grasses as it is not tolerant of shade. Grasses minimize the lodging of alsike clover by helping to keep it upright. Grass also helps to keep the clover from packing after cutting and allows air to penetrate the windrow, resulting in more rapid and thorough drying. When seed is properly inoculated at time of planting, alsike clover fixes nitrogen from N2 in the atmosphere, requiring little or no additional nitrogen fertilizer. However, it does respond to relatively large amounts of phosphorus and potassium and sometimes sulphur fertilizer applications. In grass-legume mixtures, it is not possible to supply the ideal combinations of elements for both grass and legume. If nitrogen is applied to a grass-legume mixture, the grass will tend to increase at the expense of the legume. Well-fertilized grass will outgrow clover in fall and winter and could smother the clover. Spring applications of nitrogen will stimulate grass and provide early feed, but excessive rates are detrimental to the clover stand. Phosphate applications are broadcast in fall or spring according to soil tests. Sulfur, boron, or magnesium may be needed for maximum production on some soils in the western part of the range of alsike clover. Management for forage is aimed at maintaining 40% to 50% clover. Close grazing (2 inch stubble height) favors clover, whereas light grazing favors grass. Pastures should be rotationally grazed. Alsike clover has a tendency to cause bloat and should be fed to livestock with care. On pasture high in alsike clover content, take steps to introduce animals gradually to the forage or risk of bloat can be high. It has also been implicated as causing “alsike clover poisoning” in horses but existing experimental evidence is insufficient to prove that such a poisoning exists caused by alsike clover. Alsike-induced photosensitization has been reported among animals grazing alsike clover. This will occur in bright, sunny weather and causes a reddening of the skin and swelling of the affected areas in horses. Alsike clover can be used as a cover crop in rotation with cereal grains or corn. It can be seeded with a cash crop in spring, and after the cash crop is harvested, the clover is allowed to grow until it is plowed down. The amount of commercial nitrogen fertilizer can be decreased for the succeeding crop.
Pests and Potential Problems
Alsike clover is resistant to many diseases, such as bacterial wilt, bacterial blight, mildew, and northern anthracnose, which can cause major losses in other forage legumes. Most crop losses of alsike clover can be minimized by management practices that maintain a vigorous stand. The use of clean seed and rotation with non-legume crops are the most effective to control most diseases of alsike clover. Alsike clover is subject to brown and fusarium root rot, rust, crown and stem rots, seedling blight, sooty blotch, spring black stem, stagonospora leaf spot and snow mold. Lygus bugs, aphids, and leafhoppers can cause injury to alsike clover. Weeds can be detrimental to stand establishment. It is important to prepare clean fields for planting. The use of Certified seed can reduce weed problems and crop rotation with competitive annual crops is also beneficial.
Environmental Concerns
Concerns
Concerns
Alsike clover may be spread by seed and may be considered weedy in some locations. It can spread into adjoining vegetative communities under ideal climatic and environmental conditions.
Seed Production
Plant alsike clover at 1- 3 pounds per acre PLS in 12 inch rows as early in the spring as possible. It can also be solid seeded up to 6 pounds PLS per acre for seed production. The use of a companion crop is not recommended. Diploid and tetraploid cultivars must not be mixed and each must be grown in isolation from each other. Seed yields of tetraploid cultivars can be reduced as much as 50% if they are fertilized by diploid pollen. Alsike clover must be cross-pollinated to produce seed. The honey bee is the most important pollinator of alsike clover. Two to three hives or colonies should be placed per acre. Bumble bees also pollinate alsike clover but can not be relied on because their populations fluctuate from year to year. Alsike clover should be harvested when 90% of the seedheads are brown. To obtain highest seed yields, it is usually cut and windrowed for drying prior to combining. Chemical defoliation and straight combining 5-7 days later can also be used. Seed yields average 400-500 pounds per acre. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Most of the seed available in the United States is common seed and can be obtained from commercial seed sources. Canada has several cultivars. ‘Aurora’ was released in 1961 by Agriculture Canada. It is medium to late maturing, tolerates acidic and alkaline soils and some spring flooding. It is the standard of comparison for official trials in Alberta. ‘Dawn’ was released in 1974 by Agriculture Canada and is noted for moderate resistance to mosaic virus disease. These cultivars should be adapted to most areas in the United States where alsike clover is adapted. A number of cultivars have been developed in Denmark, Norway and Sweden but are not available or used in the United States to any extent.
Control
Contact your local agricultural extension specialist or county weed specialist to determine what works best in your area and how to use it safely. Always read label and safety instructions for each control method. Trade names and control measures appear in this document only to provide specific information. USDA, NRCS does not guarantee or warranty the products and control methods named, and other products may be equally effective.
References
MacGregor, S.E. 1976. Chapter 3 clover and some relatives. IN S.E. MacGregor. 1976. Insect pollination of cultivated crop plants. USDA ARS. http://gears.tucson.ars.ag.gov/book/chap3/alsike.html [Accessed: 05December2008] Fairey, D. T. 1986. Alsike Clover. Publication 1264/E, Communications Branch, Agriculture Canada, Ottawa. 17pp. Forage Fact Sheet: Alsike Clover http://forages.oregonstate.edu/fi/topics/fact_sheet_print_legume.cfm?specid=39&use=
Forage
[2008December5] Jensen, Kevin et al. 2004. Intermountain Planting Guide. 80pp.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
Trifolium elegans Savi
Uses
Alsike clover is used for hay, pasture, and soil improvement, and is preferred where wetter or acid soils are encountered, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Trifolium hybridum L. var. pratense Rabenh.., It is generally out produced by other clover species for particular uses, Note: alsike clover can be toxic to horses under some conditions,
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
Alsike clover has smooth stems and leaves, reaching a height of 2-4 feet. This introduced plant tends to recline or lodge unless companion plants hold the stem upright. The flowers are pink to white, and are borne along the length of the stem. The flower heads are much smaller than red clover, and the stems do not terminate in a flower as they do in red clover.
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution
Distribution
Alsike is best adapted to the cool climate of the Northeast. It will tolerate wetter soils better than other clovers, and also acid conditions. It prefers silty clay loams, and does not tolerate droughty sites. Alsike clover is distributed throughout the United States. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website. USDA NRCS National Plant Materials Center Beltsville, MD
Establishment
Alsike clover is always seeded with grass, or can be overseeded into grass in the spring. For conventional plantings, spring and fall seedings will work. Alsike seed should always be inoculated due to the infrequent use of the species. Plant alsike at 2-4 pounds per acre, at a depth of 1/4 to 1/2 inch. Pre-plant fertilize according to soil test.
Management
Pasture management varies depending upon the forages in use, but should be based upon the grasses involved since they are the “meat and potatoes” of the mix. High rates of nitrogen fertilizer will damage the alsike component. In hayfields, cutting below 2 inches will damage the stand. Animal management note: on pasture high in alsike clover content, take steps to introduce animals gradually to the forage or risk of bloat can be high. Horses have done poorly on pastures that have significant alsike components.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -38 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Medium |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | Low |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 50 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | High |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.6 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 26 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 12 |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | Slight |
| Shape and Orientation | Semi-Erect |
| Nitrogen Fixation | High |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Bloat | High |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | White |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Short |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.0 |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Form | Single Crown |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed per Pound | 680400 |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Protein Potential | High |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |