Rudbeckia amplexicaulis Vahl
Scientific Name: Rudbeckia amplexicaulis Vahl

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | RUAM7 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Annual |
| Growth Habits | Forb/herb |
| Native Locations | RUAM7 |
Plant Guide
Description
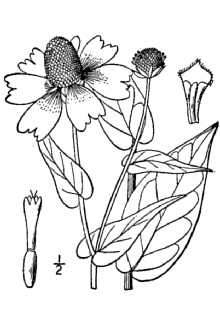
General: Clasping coneflower is a native, warm season, annual forb in the Asteraceae family (Missouri Botanical Garden, 2019). Clasping coneflower grows 12 to 28 inches (30 to 71 cm) tall. It arises from a solitary stem which branches out about half way up the plant (Fig.1). The alternately arranged, oblong, glaucous leaves are 1.75 to 4 inches (4 to 10 cm) long. The leaves, at their base, wrap around the stems (Fig.1). This distinctive leaf characteristic is the origin of the species name derived from two Latin words; amplexus meaning ‘encircling’ and caulis meaning ‘stem’. Clasping coneflower blooms in late spring and early summer. The yellow ray flowers or “petals” are similar in appearance to black-eyed Susan (Rudbeckia hirta) and droop as the flowers mature. The flowerhead is up to two inches in diameter with a black center cone 0.5 to 1.25 inches (1 to 3 cm) high. (Ajilvsgi, 2003). The seeds are small, approximately 5/64” long (2 mm), elliptical in shape, with a wrinkled appearance (USDA NRCS, 2019) (Fig.2). Distribution: Clasping coneflower is the only member of the Dracopis genus in North America (Diggs et al., 1999). It is found in the southeastern United States from Georgia to Texas and north into Missouri and Kansas (Missouri Botanical Garden, 2019). For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Clasping coneflower occurs in prairies, swales and flood plains and is found along roadsides and streams (Ajilvsi, 2003; Missouri Botanical Garden, 2019).
Adaptation
Clasping coneflower prefers sites with full sun and moist soils but not poorly drained soils (Missouri Botanical Garden, 2019). This forb tolerates various soil types including acid or calcareous based sandy or clay loams (Ladybird Johnson Wildflower Center, 2019).
Uses
Clasping coneflower is an attractive plant for native gardening and wildflower meadows because of low maintenance requirements, showy flowers, and abundant self-seeding (Missouri Botanical Garden, 2019; Ladybird Johnson Wildflower Natural Resources Conservation Service Plant Guide Figure 2. Clasping coneflower seeds. Photo: Steve Hurst, ARS, hosted by the USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database. Figure 1. Clasping coneflower in bloom. Photo: East Texas Plant Materials Center, Nacogdoches, TX 2 Center, 2019). Foraging honeybees (Apis sp.) use the Asteraceae plant family for pollen and nectar sources (Jones and Bryant, 2014). Native bees and butterflies used clasping coneflower as a nectar source (Adamson et al., 2015).
Ethnobotany
Cherokee Native Americans used clasping coneflower juice for earaches and leaves to make a tonic and diuretic tea (Ladybird Johnson Wildflower Center, 2013).
Status
Threatened or Endangered: Clasping coneflower is not listed as threatened or endangered (US Fish and Wildlife Service, 2019). Wetland Indicator: Wetland Indicator by region: (USDA NRCS, 2019) Region Indicator Region Indicator Great Plains FAC1/ Midwest FACU2/ Eastern Mountains and Piedmont FAC Northcentral and Northeast FACU Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plains FAC Arid West FACW3/ Western Mountains, Valleys, and Coast FAC 1/=Facultative -occurs in both wetlands and non-wetlands, 2/=Facultative upland-usually occurs in non-wetlands, but may occur in wetlands, 3/= usually occur in wetlands, but may occur in non-wetlands. Weedy or Invasive: This plant may become weedy or invasive in some regions or habitats and may displace desirable vegetation if not properly managed. Please consult with your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, state natural resource, or state agriculture department regarding its status and use. Please consult the PLANTS Web site (http://plants.usda.gov/) and your state’s Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g., threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Planting Guidelines
Broadcast seeding is the preferred method for planting clasping coneflower. Prepare a weed free seedbed using light tillage, herbicide applications, or close mowing. Lightly disk or harrow to loosen the soil surface then roll or cultipack prior to seeding. Broadcast seed at a rate of 4 to 5 lb pure live seed (PLS)/acre in mid to late August or September (Grabowski, 2001). Seed should be placed close to the soil surface then rolled or cultipacked after seeding.
Management
Clip or mow spent flowers to control self-seeding and/or encourage additional blooming (Missouri Botanical Garden, 2019). Clasping coneflower is a prolific reseeder, but eventually declines without soil disturbance. Disk the site every two to three years to control perennial weeds and promote clasping coneflower germination (Burgess et al., 2010).
Pests and Potential Problems
Clasping coneflower is suspectible to powdery mildew (Erysiphe sp.) (Nieland and Finley, 2009) and may form colonies and shade out accompanying vegetation (Ajilvsgi, 2003).
Environmental Concerns
Concerns
Concerns
Clasping coneflower is considered a desirable plant within its native range and has no known effects on the environment.
Control
Clasping coneflower may be controlled by mechanical means such as mowing or applying a broad-spectrum herbicide. Please contact your local agricultural extension specialist or county weed specialist to learn what works best in your area and how to use it safely. Always read label and safety instructions for each control method. Control measures appear in this document only to provide specific information.
Seed and Plant Production
Plant Production
Plant Production
Prepare a weed free seedbed using tillage and/or herbicide application. Prior to planting, the seedbed must be firmed and accumulated moisture for improved establishment success. Broadcast seed at a rate of 4 PLS/acre during August or September (Grabowski, 2001). Mix the seed with a carrier agent such as cat litter or coarse sand to improve seed distribution and help prevent planting at too high a rate. After seeding, cultipack or roll the planting site to ensure good seed-to-soil contact. Clasping coneflower seedlings emerge in fall and over winter as small plants and begin rapid growth the following spring (Grabowski, 2001). In spring, apply 15 to 30 lb/ac. of nitrogen to aid plant growth and seed production.
Literature Cited
Adamson, N,, B, Borders, J, Cruz, S, Jordan, K, Gill, J, Hopwood, E, Lee-Mader, and M, Vaughan, 2015, Pollinator plants southeast region, The Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation, Portland, OR, Ajilvsgi, G, 2003, Wildflowers of Texas, Shearer Publishing, Fredericksburg, TX, Burgess, L,, T, Moss, J, Pomerlee, and J, Allison, 2010, Fact sheet-guidelines for fall wildflower planting, Jamie L, Whitten Plant Materials Center, Coffeeville, MS, Diggs, G,M,, B,L, Lipscomb and R,J, O’Kennon, 1999, Shinner and Mahler’s illustrated flora of north central Texas, Botanical Research Institute of Texas, Ft, Worth, TX, Grabowski, J,M, 2001, Native plant network propagation protocol database: protocol information Dracopis amplexicaulis (Vahl,) Cass, Plants; Natural Resources Conservation Service – Coffeeville/Jamie L, Whitten Plant Materials Center, Coffeeville, Mississippi, In: Native Plant Network, Accessed online 12 March 2019 at: http://www,nativeplantnetwork,org Moscow (ID): University of Idaho, College of Natural Resources, Forest Research Nursery, Grabowski, J,M, 2005, Native wildflower seed production techniques in Mississippi, Native Plants Journal, Univ, Of Wisconsin Press, Vol, 6(1): pp, 72-75, Jones, G, and V, Bryant, 2014, Pollen studies of east Texas honey, Palynology, 38(2): 242-258, Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center, 2019, Native Plant Database, Accessed online 3/12/2019: http://www,wildflower,org/plants/result,php?id_plant=DRAM , Missouri Botanical Garden, 2019, Plant Finder, Accessed online 12 March 2019 at: http://www,missouribotanicalgarden,org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails,aspx?kempercode=b277 Nieland, L, and W, Finley, 2009, Lone star wildflowers – a guide to Texas flowering plants, Texas Tech Univ, Press, Lubbock, TX, Figure 3, Mature coneflower seed heads are dark brown with a woolly or fuzzy appearance,
Conservation
Service, East Texas Plant Materials Center. Nacogdoches, TX 75964. Published: June 2019 Edited: For more information about this and other plants, please contact your local NRCS field office or Conservation District at http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/ and visit the PLANTS Web site at http://plants.usda.gov/ or the Plant Materials Program web site: http://plant-materials.nrcs.usda.gov. PLANTS is not responsible for the content or availability of other Web sites. In accordance with Federal civil rights law and U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) civil rights regulations and policies, the USDA, its Agencies, offices, and employees, and institutions participating in or administering USDA programs are prohibited from discriminating based on race, color, national origin, religion, sex, gender identity (including gender expression), sexual orientation, disability, age, marital status, family/parental status, income derived from a public assistance program, political beliefs, or reprisal or retaliation for prior civil rights activity, in any program or activity conducted or funded by USDA (not all bases apply to all programs). Remedies and complaint filing deadlines vary by program or incident. Persons with disabilities who require alternative means of communication for program information (e.g., Braille, large print, audiotape, American Sign Language, etc.) should contact the responsible Agency or USDA's TARGET Center at (202) 720-2600 (voice and TTY) or contact USDA through the Federal Relay Service at (800) 877-8339. Additionally, program information may be made available in languages other than English. To file a program discrimination complaint, complete the USDA Program Discrimination Complaint Form, AD-3027, found online at How to File a Program Discrimination Complaint and at any USDA office or write a letter addressed to USDA and provide in the letter all of the information requested in the form. To request a copy of the complaint form, call (866) 632-9992. Submit your completed form or letter to USDA by: (1) mail: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue, SW, Washington, D.C. 20250-9410; (2) fax: (202) 690-7442; or (3) email: program.intake@usda.gov. USDA is an equal opportunity provider, employer, and lender.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | 32 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Medium |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fire Tolerance | None |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 120 |
| Hedge Tolerance | Low |
| Moisture Use | High |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 6.0 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 10 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 6 |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Black |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Growth Form | Single Stem |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.0 |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
Reproduction
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
|---|---|
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Seed per Pound | 1600000 |
| Seed Spread Rate | Rapid |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Small Grain | No |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Late Summer |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |