Robinia pseudoacacia L. f. inermis (Mirb.) Rehder
Scientific Name: Robinia pseudoacacia L. f. inermis (Mirb.) Rehder

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | ROPSI2 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Tree |
| Native Locations | ROPSI2 |
Plant Guide
Use a soil moisture meter to monitor the soil moisture where Robinia pseudoacacia L. f. inermis (Mirb.) Rehder is planted.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
False acacia, yellow locust
Uses
Since the wood of black locust is strong, hard, and extremely durable, it is extensively utilized for fencing, mine timbers, and landscaping ties. This tree also serves as a good erosion control plant on critical and highly disturbed areas, due to its ease of establishment, rapid early growth and spread, and soil building abilities. It has limited value in wildlife food plots, but provides excellent cover when planted in spoil areas. Due to its showy aromatic flower, it has often been planted as an ornamental, but this practice should be discouraged due to the potential for spread by root suckers. This species has been planted outside its natural range, and can crowd out other plants, particularly in sandy soils.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Weediness
This plant is considered noxious and/or invasive in some states. This plant may become weedy or invasive in some regions or habitats and may displace desirable vegetation if not properly managed. Please consult with your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, or state natural resource or agriculture department regarding its status and use. Weed information is also available from the PLANTS Web site at plants.usda.gov.
Description
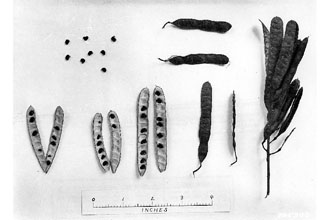
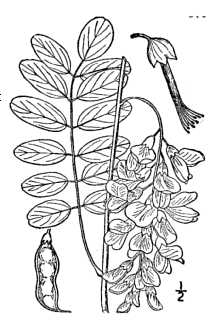
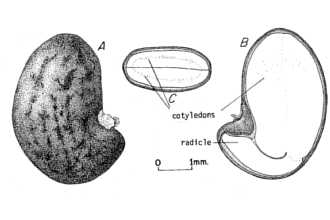
Black locust has a shallow, aggressive root system. The bark of black locust is deeply furrowed and is dark reddish-brown to black in color. It has an alternate branching pattern, which creates a zigzag effect. A pair of sharp thorns grows at each node. They are ½ to ¾ inches long, and very stout. The pinnately compound leaves are 8 to 14 inches long, with 7 to 19 short stalked leaflets. These dull green leaflets are ovoid or oval, 1 to 2 inches long, thin, scabrous above and pale below. © William S. Justice Department of Botany, Smithsonian Institution The separate male and female plants have sweetly fragrant flowers that are creamy white with five petals (bean-like) arranged in a pyramidal spike. They usually bloom in May or June. Heavy seed production can be expected annually or biannually. The legume type seed is produced in a flat, brown to black pod, which is 2 to 4 inches long. There is an average of 25,500 seeds per pound. Although black locust is a good seed producer, its primary means of spread is by both rudimentary and adventitious root suckers.
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution
Distribution
Black locust’s native range follows the Appalachian Mountains from Pennsylvania to Alabama, and a secondary population exists primarily in the Ozark Mountains. Black locust is adapted to a wide variety of soil types, but grows best on sites that are deep, well drained, and derived from limestone. This tree tolerates a pH range of 4.6 to 8.2. It is commonly found on south and west slopes in West Virginia. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website.
Establishment
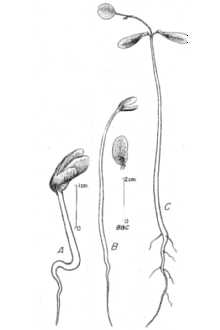
Due to the ease of vegetative reproduction, black locust is seldom grown from seed. If seedling production is desirable, the hard seed coat must first be reduced or broken to allow germination; this can be done with sulfuric acid or hot water. Once treated, the seed can be sown on raised nursery beds or directly on to field sites. Black locust seed combined in grass and legume mixtures can be broadcast, drilled, hydroseeded, or aircraft dispersed. Limit locust to 3 pounds per acre in such mixtures. Black locust is easily propagated from softwood, hardwood, and root cuttings. Preparing 6 to 12 inch hardwood cuttings, collected while dormant is often the most effective procedure. This form of cutting responds well to root-inducing chemicals. Grafting is also a viable propagation option to maintain varietal integrity.
Management
During establishment, protection from weeds and deer are the main management priorities. Due to the rapid early growth, two years of protection are usually sufficient. Pre-plant site preparation to control weeds with tillage or herbicides is recommended, with continued weed control after planting. Where exceptional deer pressure exists, tubes or mesh sleeves may be required. Once established this species will not require active management unless straight trunks are desired for fence posts- see Pests for information about controlling locust borers.
Pests and Potential Problems
There are 2 primary insects inflicting damage on black locust: locust leaf miner and black locust borer, The leaf miner attacks the tree in spring, turning the leaves brown by mid-summer or early fall, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Robinia pseudoacacia L. f. inermis (Mirb.) Rehder., Overall tree growth is impacted, but not seriously, The larvae of the locust borer carve tunnels through the trunk of the tree, weakening it enough for wind breakage, Planting on good quality sites or in conjunction with other hardwood species and shading trunks will discourage infestation by locust borers, Heart rot is the only noteworthy disease effecting black locust, Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Ornamental varieties have been developed which are available from commercial nurseries, The Steiner group black locust was selected and released by the NRCS Plant Materials Program, for critical area re-vegetation in the Appalachian region, The three cultivars in the Steiner group, 'Appalachia' (VA), 'Allegheny' (WV), and 'Algonquin' (WV) are clonally propagated,
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
|---|---|
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | Low |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 140 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 140 |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -37 |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -37 |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 36 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 36 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 20 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 16 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 65 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 160 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 160 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1200 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1200 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.8 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.6 |
| pH, Maximum | 8.2 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
Morphology/Physiology
| Active Growth Period | Spring |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Color | White |
| Flower Color | White |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Coppice Potential | Yes |
| Coppice Potential | Yes |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Active Growth Period | Spring |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Black |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Nitrogen Fixation | Medium |
| Nitrogen Fixation | Medium |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Short |
| Lifespan | Short |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 50.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 60.0 |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Black |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 40 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 40 |
Reproduction
| Propagated by Cuttings | Yes |
|---|---|
| Propagated by Seed | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Seed per Pound | 24000 |
| Seed per Pound | 24000 |
| Seed Spread Rate | Moderate |
| Seed Spread Rate | Moderate |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Moderate |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Slow |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | Yes |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Bloom Period | Spring |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Spring |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Spring |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
Suitability/Use
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
|---|---|
| Palatable Browse Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Post Product | Yes |
| Post Product | Yes |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Pulpwood Product | Yes |
| Pulpwood Product | Yes |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | Yes |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fuelwood Product | High |
| Fuelwood Product | High |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |