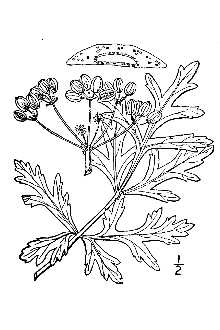
Pleiotaenia nuttallii (DC.) J.M. Coult. & Rose
Scientific Name: Pleiotaenia nuttallii (DC.) J.M. Coult. & Rose

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | PLNU |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | BiennialPerennial, |
| Growth Habits | Forb/herb |
| Native Locations | PLNU |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Texas parsley, prairie parsley
Uses
This species is used in wildflower gardens and prairie restoration.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
General: Celery Family (Apiaceae). Texas parsley is a biennial (lives two years, only flowers the 2nd year). Sometimes it is recognized as a perennial. It is most conspicuous in the months of April and May of the second year during its rapid growth and flowering period. This herb (forb) is very common along road rights-of-way and prairies in the southern, central and eastern portions of the state, but is uncommon in the “true” piney woods of deep east Texas. Polytaenia is normally from 2-4 feet in height. During spring and early summer, the vegetative portion of the plant appears to be yellowish in color. The flowers are compound umbels and are yellow. The seeds are flat, somewhat resembling rolled oats. Vascular Plant Image Gallery Texas A&M University Other umbels with similar growth habits are Queen Anne’s lace/wild carrot/rattlesnake-weed (Daucus spp.), Bishop’s weed (Ammi majus), water-hemlock (Cicuta spp.), and golden Alexanders (Zizia aurea). Daucus, Ammi and Cicuta all have white flowers. Although Zizia flowers are yellow, its leaflets are sharply serrated (saw toothed) rather than incised (cut deeply) or deeply lobed and its fruit is not flat. Zizia is not a common plant in Texas, while Polytaenia is one of the most common umbels found along roadsides in Texas.
Distribution
This species is known from North Dakota and Michigan to Texas and Alabama. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Establishment
Adaptation: Polytaenia appears to prefer well drained, loamy sites in full sun. The plant is fairly uncommon in grazed areas. Cultivars, Improved and Selected Materials (and area of origin) These plant materials are readily available from commercial sources. Contact your local Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources
Conservation
Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture,” , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Pleiotaenia nuttallii (DC.) J.M. Coult. & Rose.
References
Davis, L. 2000. Texas plant fact sheet: Polytaenia nuttallii. USDA, NRCS, Nacogdoches Technical Office #2, Nacogdoches, Texas. Texas A&M University 2001. Vascular plant image gallery. Bioinformatics Working Group, College Station, Texas. Accessed 21May2001. <http://www.csdl.tamu.edu/FLORA/imaxxapi.htm> USDA, NRCS 2000. The PLANTS database. <http://plants.usda.gov>. 001206. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.