Phleum pratense L. ssp. nodosum (L.) Arcang.
Scientific Name: Phleum pratense L. ssp. nodosum (L.) Arcang.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | PHPRN2 |
| Group | Monocot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Graminoid |
| Native Locations | PHPRN2 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Herd grass, herd’s grass, meadow cat's-tail, Phleum nodosum
Uses
Livestock: Timothy is preferred by cattle and horses, and timothy hay is a premium feed for horses. Sheep utilize timothy during the summer in mountainous areas. Timothy is used for pasture and silage, but mostly for hay. It is palatable and nutritious. It makes a first rate companion grass with alfalfa, birdsfoot trefoil, or clover species as it is one of the grasses least competitive with legumes. Erosion control: Timothy can be used with legumes and/or other grasses in seed mixtures for cover, filter strips, herbaceous buffers, waterways, and other critical area applications. It can also be used for erosion control on cut- or burned-over forestland. Keep in mind that timothy is shallow-rooted and thus should not be considered the primary species for erosion control plantings. Wildlife: Timothy is commonly found in wildlife seed mixtures for nesting, brood rearing, and escape cover.
Status
Consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Weediness
Timothy is a relatively short-lived, introduced perennial grass that grows in stools or clumps. It spreads via seed distribution. It is not considered a "weedy" or invasive species, but can spread into adjoining vegetative communities under ideal climatic and environmental conditions. It is known to coexist with native plants. On favorable sites where it is best adapted, it can exist as a monoculture. There is no documentation that it crosses with native species. It is considered a weed in seed lots in the eastern states of Delaware, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Virginia and West Virginia. Consult with your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, state natural resource, or state agriculture department regarding its status and use. Weed information is also available from the PLANTS Web site at http://plants.usda.gov/. Consult the Related Web Sites on the Plant Profile for this species for further information.
Description
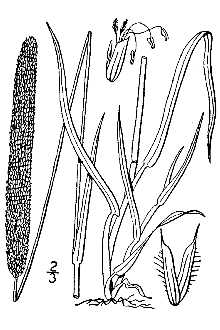
General: Grass family (Poaceae). Timothy is a relatively short-lived, cool-season, introduced perennial grass that grows in stools or clumps. It has a shallow, compact, and fibrous root system. It grows in erect culms 50 to 100 cm (20 to 40 in) tall. Leaves vary in length from a few inches to more than a foot and are about 0.6 cm (0.25 in) wide, narrowing gently toward the tip.
Adaptation
Timothy is an introduced bunchgrass adapted to cool, humid areas and to high elevations. It performs well, with moderate to high yields, on wet fertile lands. It is adapted to irrigation and areas with effective annual precipitation of at least 45 cm (18 in). It prefers finer textured soils, such as clays to clay loams to loams and is adapted to soils with a pH of 5.5 to 7.0. It is tolerant of partially shaded conditions. Timothy is very winter-hardy. It exhibits tolerance to both cold temperature, and ice encasement, a major factor affecting winter survival. It is not well adapted to wet, flat land where water stands for extended periods of time, though it can withstand somewhat poorly-drained soils. It does not tolerate drought or prolonged high temperatures and it does not tolerate alkaline conditions. Timothy is compatible in mixes with legumes. It establishes cover quickly, volunteers readily on preferred sites, is late maturing, and is very palatable early in the growing season (jointing stage) and only moderately palatable later in the growing season (post seedhead development). Timothy hay is a premium feed for horses and is compatible in legume mixes. Severe damage can result from early grazing under wet conditions. It regrows very slowly following grazing or haying. Other recommended sites include cool, moist meadows and open forests. Timothy establishes quickly and volunteers readily on preferred sites. It invades wet areas along ditches, canals, drains, and streams and can be a weed in these areas.
Establishment
Timothy is usually seeded in mixtures with legumes, This mixture may be planted with a small grain, If planted with a winter grain, the timothy is seeded with the grain in the fall, and the legume is planted early the following spring, Seeding depth of timothy should be about 0,3 to 1,3 cm (0,125 to 0,5 in), A firm, weed-free seedbed is a key to a successful planting, Common seeding rates are 3 to 6 pounds per acre when seeded alone and 1 to 3 pounds per acre when seeded in mixtures, The average number of seeds per square foot at 1 lb, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Phleum pratense L. ssp. nodosum (L.) Arcang.., seeding rate is 28 seeds, Seeding rates should be doubled if seed is broadcast planted,
Management
Timothy is a short-lived, shallow-rooted, introduced, perennial bunchgrass. In spring, the crowns form swollen, bulblike internodes that store energy. Close grazing and trampling during moist conditions can damage these internodes and severely reduce stands. Timothy should be grazed before the jointing stage and hayed before seed heads have emerged from boot to early bloom stage. Begin grazing during the vegetative stage, after grass has reached at least 15 cm (6 in) in height. A 10 cm (4 in) stubble height should remain following grazing. It regrows slowly following grazing or haying. A 28 to 35 day recovery period between grazing or haying cycles is recommended. Timothy is highly responsive to fertilizers, which should be applied frequently based in accordance with soil tests. Fertilizer, especially nitrogen, is important when legumes such as clover species have almost disappeared from the hay or pasture mixture. Timothy stands become weak under close and continuous grazing. A fundamental reason for the decline of timothy under poor grazing practices is injury to the bulblets (haplacorm). These bulblets form in the spring at the same time the stem elongates. Food reserves are stored in the bulblets, and they may be destroyed through trampling by grazing animals in the spring. Timothy can be initially grazed before jointing and again between early head to full head. Second and successive grazing periods should occur before jointing and when basal sprouts appear at the soil surface. After the second grazing period, plants usually do not joint; therefore, sprouts are the primary grazing guide. Timothy should be cut for hay or silage from boot stage to early head or flowering stage. Make successive harvests for hay and silage when basal sprouts appear at the soil surface. Sterile seed-heads may be 38 to 50 cm (15 to 20 in) up the stems when sprouts appear at the time of second cutting. Growing points stay below ground level after the second cutting. Graze or cut to heights of 10 cm (4 in) or more.
Pests and Potential Problems
Stem rust is a disease that can cause loss of vigor and forage quality to timothy. Rust-resistant varieties have been developed to control this disease. Purple eyespot (Cladosporium phlei) and leaf streak (Drechslera phlei) are diseases commonly found across western Canada. Timothy is also damaged by brown leaf blight and grasshoppers. New fields are also susceptible to wireworm or cutworms. European skipper larvae (a bright orange butterfly) are a pest of timothy in eastern Canada.
Seed Production
Seed production fields should be soil tested before planting to determine soil nutrient levels and fertilizer needs. Seed should be drilled or broadcast into a weed free, firm seedbed. The optimum seeding depth is 0.3 to 1.3 cm (0.125 to 0.5 in). The drill seeding rate of 1 to 2 pounds PLS per acre in 45 to 60 cm (18 to 24 in) rows provides a good stand. Wider row spacing may be beneficial to seed production in dry climates. Under irrigated conditions, seed yields average 450 to 670 kg/ha (400 to 500 lb/ac). Seed production under dryland conditions is not recommended in the western United States. In the eastern United States, seed production yields of 336 to 450 kg/ha (300 to 400 lb/ac) can be expected. Timothy shatters readily but should not be swathed too soon. It is usually ready to swath when 5 to 10 percent of the seed have shattered (late July to early August). The seedheads will have a tan color and the stems and leaves will be a golden color. Swathing early in the morning will help reduce seed shatter. Allow 5 to 14 days of drying before combining. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Most of the timothy grown in the U.S. is common timothy. Improved cultivars and places of development are: ‘Essex’ and ‘Cornell 1777’ (New York); ‘Lorain’ and ‘Marietta’ (Ohio); ‘Itasca’ (Minnesota); ‘Clair’ (Kentucky), and ‘Verdant’ (Wisconsin). Canadian releases are ‘Bounty’, ‘Climax’, ‘Drummond’, ‘Medon’, ‘Milton’, ‘Paton’, and ‘Swallow’. Common timothy and most cultivars can be readily obtained from commercial sources. There are many proprietary timothy varieties grown under contract for seed companies.
Fact Sheet
Uses
Livestock: Timothy is used for pasture (although other cool-season grasses are preferred) and silage, but mostly for hay. It is palatable and nutritious. It makes a first rate companion grass for alfalfa, trefoil, or clover as it is the grass least competitive with legumes. Erosion control: Timothy can be used with legumes and/or other grasses in a mix for cover purposes, filter strips, waterways, and other critical area applications. Wildlife: Timothy is commonly found in wildlife mixtures for nesting, brood cover, and escape.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
Phleum pratense L., timothy, is a relatively short-lived, cool-season perennial that grows in stools or clumps and has a shallow, compact, and fibrous root system. It grows in erect culms 20 to 40 inches tall. Leaves vary in length from a few inches to a foot and are about 1/4 inch wide, narrowing gently toward the tip. Heads are spike-like and dense, from 2 to 6 inches in length. Seed is very small and usually remains enclosed in the glumes. There are approximately 1,230,000 seeds per pound. Timothy is different from most other grasses in that 1 or occasionally 2 of the basal internodes of the stem swell into a bulb-like growth. This characteristic is often used for identification of the plant during its early stages of growth.
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Phleum pratense L. ssp. nodosum (L.) Arcang..
Distribution
Timothy is adapted to a cool and humid climate. Timothy thrives best on rich, moist bottomlands and on finer textured soils, such as clay loams. It does not do well on coarser soils. It prefers a pH of 5.5 to 7.0. Timothy will grow for a time on soils low in fertility, but it is better adapted to a high fertility soil. It is not well adapted to wet, flat land where water stands for any considerable time, though it can withstand somewhat poorly-drained soils. Under limited moisture conditions, it makes a poor recovery and it does not tolerate drought or prolonged high temperatures. James R. Johnson USDA NRCS 1992 Western Wetland Flora @ USDA NRCS PLANTS Timothy is distributed throughout the entire United States. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website.
Establishment
Timothy is usually seeded in mixtures with legumes. This mixture may be drilled with a small grain. If planted with a winter grain, the timothy is seeded with it, and the legume is planted early the following spring. Seeding depth of timothy should be 1/2 inch. A firm, weed-free seedbed is a key to a successful planting. Common seeding rates are 8 to 10 pounds per acre when seeded alone and 4 to 6 pounds per acre when seeded in mixtures.
Management
Timothy is highly responsive to fertilizers, which should be applied frequently in ample quantities. Fertilizer, especially nitrogen, is important when legumes have almost disappeared from the hay or pasture mixture. Timothy stands become weak under close and continuous grazing. A fundamental reason for the decline of timothy under poor grazing practices is injury to the bulblets. These bulblets form in the spring at the same time the stem elongates. Food material is stored in them, and they may be destroyed by trampling of grazing animals. Timothy can be initially grazed before jointing and again between early head to full head. Second and successive grazing should also occur before jointing and when basal sprouts appear at the soil surface. After the second grazing, plants usually do not joint; therefore, sprouts are primary guides. Timothy should be cut for hay or silage from early to full head. Make successive harvests for hay and silage when basal sprouts appear at the soil surface. Sterile seed-heads may be 15 to 20 inches up the stems when sprouts appear at the time of second cutting. Growing points stay below the ground line after a second cutting. Graze or cut to heights of 3 inches or more.
Pests and Potential Problems
Stem rust is a disease that can cause loss of vigor and forage quality to timothy. Rust-resistant varieties have been developed to control this disease. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Most of the timothy grown in the Northeast U.S. is unimproved common timothy. Improved cultivars and places of development are: ‘Essex’ and ‘Cornell 1777’ (New York); ‘Lorain’ and ‘Marietta’ (Ohio); ‘Itasca’ (Minnesota); and ‘Clair’ (Kentucky). Canadian developments are ‘Climax’, ‘Drummond’, ‘Medon’, and ‘Paton’. Common timothy and most cultivars can be readily obtained from commercial sources.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
|---|---|
| Fertility Requirement | High |
| Fertility Requirement | High |
| Fertility Requirement | High |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | High |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 95 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 90 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 90 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 90 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 90 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 126 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 120 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 100 |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | High |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | High |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -43 |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 35 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 35 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 32 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 32 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 32 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 24 |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -43 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -38 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -38 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -38 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -33 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -33 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -33 |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intermediate |
| Shade Tolerance | Intermediate |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.8 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 65 |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 65 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 55 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 55 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 50 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 50 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 50 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 45 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.6 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.3 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.0 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.0 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.0 |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Maximum | 8.4 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.6 |
Morphology/Physiology
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
|---|---|
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Flower Color | Green |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Yellow-Green |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Rapid |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Rapid |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Rapid |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Rapid |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Rapid |
| Bloat | None |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| C:N Ratio | Low |
| Bloat | None |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Known Allelopath | Yes |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 3.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 3.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.6 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.5 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.5 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.5 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.3 |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.2 |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
Reproduction
| Propagated by Sod | No |
|---|---|
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Small Grain | No |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed per Pound | 1163200 |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Spring |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Spring |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Spring |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Spring |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Bloom Period | Early Spring |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Bloom Period | Mid Spring |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
Suitability/Use
| Palatable Human | No |
|---|---|
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Post Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Fodder Product | Yes |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |