Nyssa sylvatica Marshall var. biflora (Walter) Sarg.
Scientific Name: Nyssa sylvatica Marshall var. biflora (Walter) Sarg.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | NYSYB |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Tree |
| Native Locations | NYSYB |
Plant Guide
Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Nyssa sylvatica Marshall var. biflora (Walter) Sarg..
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
Nyssa sylvatica Marsh, var, biflora (Walt, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Nyssa sylvatica Marshall var. biflora (Walter) Sarg..,) Sarg,, blackgum, swamp blackgum
Uses
Wildlife: Its foliage and twigs are widely browsed by white-tailed deer. Fruits are highly nutritional and eaten by a variety of birds and small mammals. Additionally, provides cavity and nesting sites for a wide variety of birds and mammals. Its flowers are a source of nectar for bees kept by commercial honey producers. Timber: Used mainly for lumber, veneer, paper pulp, and to some extent railroad ties. It is also used for flooring, rollers in glass factories, blocks, gunstocks, and pistol grips. Recreation and Beautification: Excellent ornamental plant for its straight bole, shapely crown and attractive autumn foliage.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
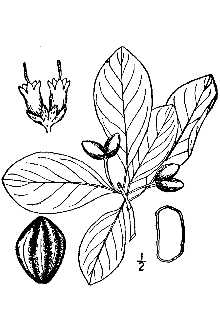
Nyssa biflora (Walt.), swamp tupelo, is limited to Coastal Plain swamps and estuaries from Maryland and southeastern Virginia south to southern Florida. It grows on the east side of the Mississippi River to western and southern Tennessee. A moderately large tree, it can grow to over 100 feet in height and 3 to 4 feet in diameter; it has a narrow, oblong crown and spreading root system which commonly produces vigorous sprouts. Bark is light brown, deeply furrowed with scaly longitudinal ridges. Leaves are alternate, simple, dark green and shiny above, paler and often hairy below.
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution
Distribution
Swamp tupelo grows well on a variety of wet bottomland soils including organic mucks, heavy clays, and wet sands. Best growth is achieved on sites where the soil is continuously saturated with very shallow moving water such as banks of swamps, ponds, and estuaries of the Coastal Plain, and in low coves and seepages which remain wet year-round. Robert H. Mohlenbrock USDA NRCS 1991 Southern Wetland Flora @ USDA NRCS PLANTS Swamp tupelo is distributed throughout the Southeast. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website.
Establishment
Stump sprouting is common following logging. It is classed as intolerant to shade and will not develop unless released. Swamp tupelo is a prolific seed producer. Seed viability averages 60 percent, increasing as the season progresses. Seeds are disseminated primarily by gravity and birds, others generally fall to the ground and remain dormant in the litter or are carried by water. Seed overwinters on cool, damp soil and germinates the following spring. It requires nearly full sunlight for optimum early growth. Seedlings tolerate more competition but are much less adaptable than black tupelo. Prechilled seeds must be sown in spring. Seeds are drilled at the rate of 15 per foot of row and covered with ½ - 1 inch of soil. A mulch of pine needles is recommended. Beds must be kept moist. It sprouts from the stump following disturbance. Sprouts arise from suppressed buds and are concentrated near the top of the stump. Stump sprouts can produce seeds at 2 years of age.
Management
Seedling establishment is best accomplished by shelterwood method. Regeneration can also be accomplished by clear-cutting if prior to a good seed fall or if advanced regeneration already exist. Due to the high palatability of seedlings and sprouts, swamp tupelo must be protected by controlling deer populations. It often competes with loblolly and shortleaf pine for water and light, reducing its growth and development. Basal tree injections with approved herbicides are effective control methods for crown kill.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -18 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | High |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | None |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Drought Tolerance | None |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 230 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | High |
| pH, Maximum | 5.7 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.5 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 800 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 400 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 40 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 34 |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Coppice Potential | Yes |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Green |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 115.0 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 36 |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Single Stem |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Blue |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Low |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Seed per Pound | 2400 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Late Spring |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | Yes |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Medium |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | Yes |
| Fuelwood Product | Medium |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |