Larix alaskensis W. Wight
Scientific Name: Larix alaskensis W. Wight

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | LAAL6 |
| Group | Gymnosperm |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Tree |
| Native Locations | LAAL6 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
American larch, eastern larch, Alaska larch, hackmatack
Uses
The commercial value of tamarack wood is limited because of insect and disease problems and its relatively poor pulping properties. The wood is used principally for pulp products, especially the transparent paper in window envelopes, but slow-growing trees develop wood with high resin content, making it decay resistant and useful for posts, poles, railroad ties. It also has been used for rough lumber, fuelwood, and boat construction. The back contains a tannin that has been used for tanning leather. Various wildlife eat the seeds, seedlings, and bark and birds use the trees for nesting.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status, such as, state noxious status and wetland indicator values.
Description
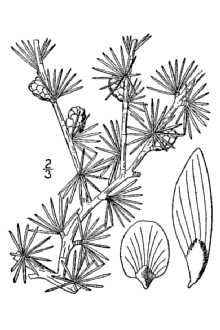
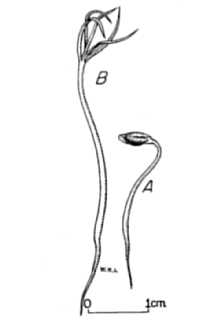
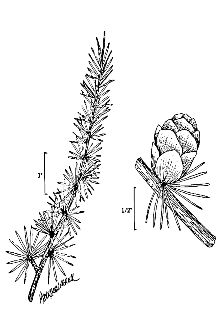
General: Pine Family (Pinaceae). Native trees growing to 20 meters tall, strongly self-pruning, with a straight, slender trunk and narrow, open, pyramidal crown that occupies one-third to one-half the bole length 25-30 years; branches whorled, horizontal or slightly ascending; short (spur) shoots prominent on twigs 2 years or more old. Bark of young trees is gray, smooth, becoming reddish brown and scaly. Leaves are deciduous, needlelike, 1-2 cm long, pale blue-green, produced in clusters on short shoots or singly along the long shoots, yellowing and shed in the fall. Seed cones are 1-2 cm long, upright; seeds winged, the bodies 2-3 mm long. The common name is the Algonquian Indian name for the plant. R. Mohlenbrock USDA, NRCS, Wetland Science Institute @ PLANTS Variation within the species: the Alaskan populations of Larix laricina have been described as a different species (Larix alaskensis = Larix laricina var. alaskensis) on the basis of narrower cone scales and bracts, but the variability is now generally recognized as within the range of other populations of the species. Genetic differences in photoperiodic response, germination, and growth patterns have been documented among trees taken from various parts of the species range. Artificial hybrids have been created between tamarack (L. laricina) and two related species: Japanese larch (L. leptolepis) and European larch (L. decidua). Tamarack differs from the other two native species of larch (Larix species) in its shorter leaves (of short shoots), shorter seed cones with fewer scales, longer scales than bracts at maturity, and broader, more northern distribution. The larches are the only deciduous conifers besides the bald cypress species.
Distribution
Across North America, from St. Pierre and Miquelon, Newfoundland, and New Brunswick, north and west to Keewatin, Mackenzie, British Columbia, and Yukon, with disjunct populations in northern Alaska; in northeastern United States from Maine to West Virginia and Minnesota. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Establishment
Adaptation: Tamarack grows in boreal forests in wet, poorly drained sphagnum bogs and muskegs, also on moist upland mineral soils, the drier sites in the northern part of its range, at elevations of 0-1200 meters. Because it can withstand high soil moisture, high acidity, and low soil temperature, it is more abundant on peatlands than trees characteristic of surrounding uplands. Planting: Tamarack trees may bear viable seed at 12-15 years of age, but open-grown trees 50-150 years old produce the best cone crops. Good seed crops are produced at intervals of 3-6 years. Germination percentages in nature often are very low, because of predation by rodents and damage by fungi or bacteria. The best seedbed is warm, moist mineral soil or organic soil with no brush but a light cover of grass or other herbaceous vegetation. For best growth, seedlings need full light and a constant water level. Early seedling mortality may be caused by damping-off, drought, drowning, and inadequate light. Under favorable conditions, tamarack is the most rapidly growing boreal conifer until it reaches about 40-50 years old. Most trees show features of senescence by 150-180 years of age, but some are known to have reached 230-240 years, and one is known to be over 335 years.
Management
Tamarack is a shade-intolerant pioneer, It is generally the first forest tree to invade filled-lake bogs and burned sites in boreal forest, but it is overtaken in succession by black spruce and various other species, As a consequence, commercial production of tamarack requires site preparation, such as slash disposal and herbicide spraying, and some form of even-age management, Trees should be planted at wide spacings, Tamarack is highly susceptible to fire damage because of the thin bark, even light burns on peatlands are destructive because of the shallow root system, Flooding from wetland road crossings and beaver dams can kill tamarack stands, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Larix alaskensis W. Wight.,
Pests and Potential Problems
Defoliation by the larch sawfly and the larch casebearer often cause extensive mortality, but imported parasites of these insects apparently are becoming established and may help to control outbreaks. Cultivars, Improved and Selected Materials (and area of origin) These plant materials are readily available from commercial sources. Contact your local Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources
Conservation
Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”
References
Brown, K.R., D.B. Zobel, & J.C. Zasada 1988. Seed dispersal, seedling emergence and early survival of Larix laricina (DuRoi) K. Koch in the Tanana Valley, Alaska. Can. J. For. Res. 18:306-314. Johnston, W.F. 1990. Larix laricina. Pp. 141-151, IN: R.M. Burns and B.H. Honkala. Silvics of North America. Volume 1. Conifers. USDA Forest Service Agric. Handbook 654, Washington, D.C. <http://willow.ncfes.umn.edu/silvics_manual/Table_of_contents.htm> Parker, W.H. 1993. Larix. Pp. 366-368, IN: Flora of North America, north of Mexico. Vol. 2, Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms. Oxford Univ. Press, New York. <http://hua.huh.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/Flora/flora.pl?FLORA_ID=12395> Parker, W.H. & T.A. Dickinson 1990. Range-wide morphological and anatomical variation in Larix laricina. Canad. J. Bot. 68:832-840.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -79 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fire Tolerance | None |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 73 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 6.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.5 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1200 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 430 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 55 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 7 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 12 |
| Salinity Tolerance | Low |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Red |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Dark Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 80.0 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 20 |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Form | Single Stem |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Seed per Pound | 292615 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Mid Spring |
| Propagated by Cuttings | Yes |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | Yes |
| Post Product | Yes |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | Yes |
| Fuelwood Product | Medium |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |