Jersey Tea
Scientific Name: Ceanothus herbaceus Raf.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | CEHE |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Shrub |
| Native Locations | CEHE |
Plant Guide
Alternative Names
red root, grub root , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Jersey Tea.
Uses
Ethnobotanic: The root of Jersey tea was used by the Chippewa for a cough remedy. They would grate approximately 5 inches of the root and mix it with water. The Lakota used the leaves of the plant to brew tea.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
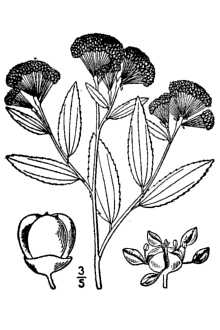
General: Buckthorn Family (Rhamnaceae). Jersey tea is a bushy shrub reaching up to one meter in height. The leaves are elliptical-oblong shaped to inversely lanceolate and are attached at the narrower end. The Plant Materials <http://plant-materials.nrcs.usda.gov/> leaves are serrated with rounded teeth along the margins. Veins arise unevenly just above the leaf base. The upper leaf surface is almost smooth. The lower leaf surface has long, soft, unmated hairs. The stalk of the inflorescence is 1-2 cm long and is racemose with flowers maturing from the bottom upwards. The flowers are white and have 5 petals (1.5 mm long), 5 stamens, and 3 lobed ovaries. The fruits or capsules are 3-4.5 mm wide and open at maturity to release the seeds. The seeds are 2 mm long, brownish in color, and have a glossy surface. Distribution: For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Jersey tea is found on rocky and open wooded hillsides and in prairies.
Establishment
Jersey tea is a drought tolerant species that grows best in well-drained soils and in full sun. Jersey tea is difficult to transplant, therefore propagation by seed is recommended. Seeds can be planted in the late fall or early winter. To plant seeds in the spring, soak the seeds overnight in warm water and stratify.
Management
Please consult your local land management agency, as this plant is listed as threatened in many states.
Pests and Potential Problems
Jersey tea is susceptible to leaf spot and powdery mildew, however no serious insect or disease problems exist. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) These materials are readily available from commercial plant sources. Contact your local Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil
Conservation
Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources Conservation Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”