Inodes schwarzii O.F. Cook
Scientific Name: Inodes schwarzii O.F. Cook

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | INSC |
| Group | Monocot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Tree |
| Native Locations | INSC |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Palmetto, cabbage palm, cabbage tree, sabal palm, blue palm, , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Inodes schwarzii O.F. Cook.
Uses
Ethnobotanic: The Seminole, Houma, Choctaw, and other Native American peoples in the southeastern United States used cabbage palmetto for a wide variety of purposes. The white, crisp palm hearts were eaten either raw or cooked by boiling or steaming. The leaf buds are purported to taste like cabbage. However, both of these food uses--the heart and the buds--result in the death of the plant. The palm fruits, which ripen in the fall, are small and mostly seed, but they are sweet with a slight bitter aftertaste. The seeds and berries were used for headaches and to lower fevers. The plants provided fiber and wood used to construct houses, make food paddles, drying frames for animal skins, potato drying mats, fish drags, fish poison, ballsticks, arrows and hunting dance staffs. Most Seminole homes were built from the cabbage palm. Logs would be used as poles for the framework of huts that were thatched with the fan-shaped leaves. Split logs were used for flooring. Immature fronds were bleached in the sun, cut into strips, and plaited to make long strips, which were used for lashing or sewn together to make baskets. The stiff midribs of the leaves were sometimes used to construct ball sticks or racquets. Palmetto-thatched houses may still be found in Houma country in Louisiana. Wildlife: Fruits ripen in the late fall and are eaten by crows, mockingbirds, warblers, pileated and red-bellied woodpeckers and squirrels. Palmetto fruits provide 10% to 25% of the diet of raccoons and robins in the Southeast. © Palm & Cycad Societies of Florida
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
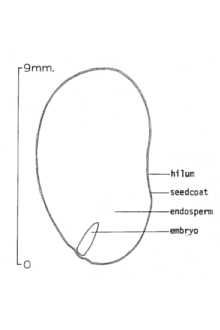
General: Palm family (Arecaceae). Cabbage Palmetto is an evergreen palm tree that can reach 20m in height. The erect, unbranched trunk has grayish to brownish bark with distinctive pineapple-like markings where the old leaf stalks were attached. Medium-green, stiff, fanlike leaves are palmately compound and spread in all directions as they emerge from the top of the trunk. The fans, often wider than they are long (2-3 m wide), contain several long and pointed leaflets with prominent midribs. During June and July, abundant, small (.5cm), fragrant, white flowers are borne upon drooping, branched clusters. The berry-like fruits are small (1.5cm), shiny and black. Each fruit contains one seed. Similar species: The shrub-like, dwarf palmetto (Sabal minor) is common to freshwater wetlands of the southeastern United States. The leaves lack the prominent midrib and it usually does not grow a stem. Distribution: Native to the Gulf Coast states and Florida. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Adaptation
Cabbage palm grows in a wide variety of habitats in which the water table is fairly close to the surface. It is found in the drier, upland areas of both fresh and saltwater wetlands, wet hammocks, riverbanks, seasonally wet prairies, maritime forests and coastal plains. In Florida and across the gulf states, cabbage palmetto is commonly found in transition zones between active floodplains and uplands. It also occurs in maritime heath communities in the Carolinas and Virginia as well as the hardwood upland hammocks communities of the Everglades.
Establishment
Cabbage palmetto is widely planted for landscaping as an ornamental because of its stately structure and large, graceful fan-shaped fronds. It has a slow to moderate growth rate and is used for street trees as well as for the patio or terrace. It can be grown in sun or in part shade. The tree grows well in a wide variety of soils with medium to poor drainage and fertility in both moist and fairly dry areas. It is recommended for seaside plantings, as it is tolerant of salt. It is not hardy in mountain areas as it is sensitive to cold. Propagation by seeds: The trees may be easily propagated from seed, as they germinate readily. Transplantings: It is best to transplant cabbage palmettos in June or July. Seedlings can be transplanted the year following germination although larger plants transplant more easily. This is because increased food reserves stored in the main stem of larger transplants help in the regeneration of new roots. Tie the leaves together before transplanting to protect the terminal bud. After transplanting into a hole large enough to hold the roots, support the plant with stakes. It is necessary to water frequently until you can observe growth, to ensure proper establishment of the root system.
Management
Established plants tend to self-sow. Fruit drupes may be removed if self-sowing is not desired. The plant has no serious pests. Remove old leaf bases to control their use as hiding places for roaches and other insects. Cultivars, Improved and Selected Materials (and area of origin) These plant materials are somewhat available from commercial sources. Contact your local Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources
Conservation
Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”
References
Bailey, L.H. & E.Z. Bailey 1976. Hortus Third: A concise dictionary of plants cultivated in the United States and Canada. Simon and Schuster Macmillan Co., New York, New York. 1290 pp. Barbour, M.G. & W.D. Billings, Editors 2000. North American terrestrial vegetation, Second Edition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom. 708 pp. Brown, R.C. 1994. Florida’s first people: 12,000 years of human history. Pineapple Press, Inc., Sarasota, Florida. 262 pp. Chapman, A.W. 1883. Flora of the Southern United States: Flowering Plants and Ferns. Second Edition. J. Wilson and Son, Cambridge, Massachusetts. 698 pp. Flint, H.L. 1997. Landscape plants for Eastern North America. Second Edition. John Wiley and Sons, New York, New York. 842 pp. Godfrey, R.K. & J.W. Wooten 1979. Aquatic and wetland plants of Southeastern United States. Vol. 1. University of Georgia Press, Athens, Georgia. 712 pp. Halfacre, R.G. & A. R. Showcroft 1979.
Landscape
plants of the Southeast. Sparks Press, Raleigh, North Carolina. 325 pp. Kniffen, F.B., H.F. Gregory & G.A. Stokes 1994. The historic Indian Tribes of Louisiana. Louisiana State University Press, Baton Rouge, Louisiana. 324 pp. Martin, A.C., H.S. Zim & A.L. Nelson 1951. American wildlife and plants: A guide to wildlife food habits. Dover Publications, New York. 500 pp. Moerman, D.E. 1998. Native American ethnobotany. Timber Press, Portland, Oregon. 927 pp. Neill, W.T. 1956. The story of Florida’s Seminole Indians. Second Edition. Great Outdoors Publishing Co., St. Petersburg, Florida. 128 pp. Ottesen, C. 1995. The native plant primer. Harmony Books, New York, New York. 354 pp. Palm & Cycad Societies of Florida 2000. Sabal palmetto. Accessed: 21May2001. <http://www.plantapalm.com/vpe/photos/Species/sabal_palmetto.htm> Rogers, D.J. & C. Rogers 1991. Woody ornamentals for Deep South gardens. University of West Florida Press, Pensacola, Florida. 296 pp. Small, J.K. 1933. Manual of Southeastern flora. University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1554 pp. Sturtevant, W.C. 1954. The Mikasuki Seminole: medical beliefs and practices. Doctoral Dissertation, Yale University. 538 pp. Tiner, R.W. 1993. Field guide to coastal wetland plants of the Southeastern United States. University of Massachusetts Press, Amherst. 328 pp. Whitcomb, C.E. 1983. Know it and grow it, II: A guide to the identification and use of landscape plants. Lacebark Publications, Stillwater, Oklahoma. 740 pp.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | 16 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Medium |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fire Tolerance | Low |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 180 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 7.8 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.1 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1200 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 300 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 70 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 18 |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Shade Tolerance | Tolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Climbing |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | Yes |
| Flower Color | White |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Color | Gray-Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Dense |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Leaf Retention | Yes |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 90.0 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 15 |
| Growth Rate | Slow |
| Growth Form | Single Stem |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Black |
Reproduction
| Small Grain | No |
|---|---|
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed per Pound | 1675 |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Winter |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Commercial Availability | No Known Source |
| Bloom Period | Summer |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | Yes |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fuelwood Product | Low |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |