Homalocenchrus virginicus (Willd.) Britton
Scientific Name: Homalocenchrus virginicus (Willd.) Britton

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | HOVI4 |
| Group | Monocot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Graminoid |
| Native Locations | HOVI4 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Whitegrass, White Grass, Virginia Cutgrass, Virginian Cutgrass, White Cutgrass, Leersie De Virginie
Uses
Whitegrass is highly palatable to grazing and browsing animals. However, it grows in wet, wooded areas that are not optimum pasture areas. Wildlife: The caterpillars of the butterfly Enodia anthedon (Northern Pearly Eye) feed on the foliage of whitegrass. Aside from this, little is known about floral-faunal relationships for this species.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Homalocenchrus virginicus (Willd.) Britton.,g,, threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values), USDA Native Status: L48 (N), CAN (N),
Description
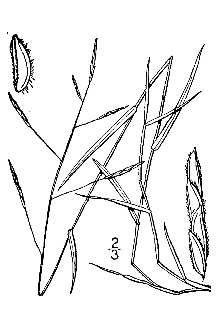
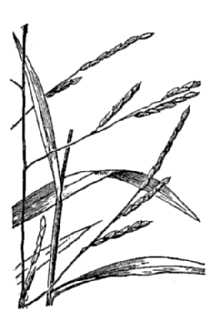
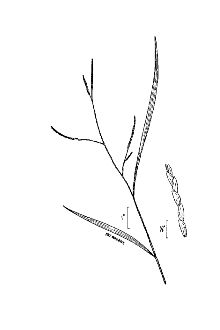
General: Grass Family (Poaceae) Whitegrass is a perennial grass that is native to eastern North America. It is 1 – 3 feet tall, branching occasionally; it is erect to spawling and flowers from July to October. Whitegrass is a good example of the kinds of grasses that grow in wooded areas. Such grasses usually have delicate tin-textured foliage and their panicles or racemes are slender and lanky with small spikelets. As a general rule, they are not very showy. Whitegrass is fairly easy to identify because its spikelets are appressed together to form a single row along the upper half of each branchlet. Each spikelet is single-flowered, oblongoid, and often ciliate along the margins of its lemma. Each floret of whitegrass produces only 2 anthers; this is unusual, because most grasses produce 3 anthers per floret. It is easily confused with the non-native and invasive Japanese stilt grass (Microstegium vimineum). Whitegrass may be distinguished from Japanese stilt grass by its lack of a prominent shiny leaf midvein. It has a short life span relative to most other plant species and a moderate growth rate. Distribution: Whitegrass is typically found in partially shaded low-lying wet areas. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Moist, shady areas in wooded sites of fertile loamy soil with abundant organic matter, typically along water bodies.
Adaptation
Whitegrass grows in USDA Hardiness Zones 2 through 11. It is shade tolerant and grows best in coarse to medium textured soils in moist areas.
Establishment
Whitegrass may be propagated from seeds or by plant division (rhizomatous). The blooming period occurs from mid-summer to early fall. Each floret develops a single grain. It has a slow ability to spread through seed production and the seedlings have medium vigor. Cold stratification is not required for seed germination and the plant cannot survive exposure to temperatures below – 43 degrees F and is not tolerant to drought. Whitegrass can be propagated by plant division through digging and mechanically dividing the rhizomatous root ball into sections. The root system has scaly rhizomes (underground stems) and fibrous roots. This grass occasionally forms vegetative colonies from its rhizomes.
Management
Whitegrass does not require fertilization but thrives in fertile lowlands.
Pests and Potential Problems
There are no known pests of this native grass. Whitegrass is not known to spread in an invasive manner.
Seeds and Plant Production
Plant Production
Plant Production
Seeds or bare roots may be obtained at nurseries or garden centers. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Contact your local Natural Resources
Conservation
Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under United States Government. The Natural Resources Conservation Service should be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”
References
Leersia virginica, Willd. Enclopedia of Life. Accessed 12 March 2012. Available at http://eol.org/pages/1114464/overview (verified March 2012). Gardenguides.com. Copyright 1997-2010. Whitegrass (Virginica). Accessed 12 March 2012. Available at http://www.gardenguides.com/taxonomy/whitegrass-leersia-virginica/ (verified March 2012). Strasbaugh, P. D.and E. L. Core. 1952. Flora of West Virginia. West Virginia University Bulletin, series 65, No. 3-1, p. 99-100. Morgantown, West Virginia,100p. Hilty, John . Copyright 2002-2012. Illinois Wildflowers. Leersia virginica. Accessed 12 March 2012.Available at http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/grasses/plants/white_grass.htm USDA, NRCS. 2012. The PLANTS Database(http://plants.usda.gov, 12 March 2012). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27402-4901 USA. (verified March 2012).
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -43 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Medium |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | None |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | None |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 120 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 8.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.5 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 19360 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 10912 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 65 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 15 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 4 |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Tolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring |
| Bloat | None |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Green |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Red |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | Yes |
| Lifespan | Short |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 3.9 |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Rhizomatous |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Texture | Fine |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Late Summer |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | High |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |