Cyanococcus corymbosus (L.) Rydb.
Scientific Name: Cyanococcus corymbosus (L.) Rydb.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | CYCO15 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Shrub |
| Native Locations | CYCO15 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Northern highbush blueberry, southeastern highbush blueberry, Maryland highbush blueberry, black highbush blueberry, American blueberry, New Jersey blueberry, rabbiteye blueberry, swamp blueberry, tall huckleberry, mayberry, whortleberry
Uses
Highbush blueberry is the major blueberry of commerce. It is extensively cultivated in New Jersey, Michigan, North Carolina, and Washington and to a lesser extent in Georgia, Florida, Indiana, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, Massachusetts, British Columbia, Ontario, Quebec, and Nova Scotia. In 1989, there were over 100,000 acres in commercial fruit production in North America. More than 50 cultivars highbush blueberry have been developed, primarily based on selections for commercially valuable fruit characteristics and seasonality. Good summaries of information relating to commercial fruit production are available (see Reiger 2000; Garrison 1998). A few selections are used in landscaping, especially where they might be planted in wet places and to attract wildlife. The berries are eaten raw, smoke-dried, sun-dried, boiled, and baked -- in a wide variety of culinary settings. They have one of the highest concentrations of iron of the temperate fruits. The fruits provide important summer and early fall food for numerous species of game birds, songbirds, and mammals.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status, such as, state noxious status and wetland indicator values.
Description
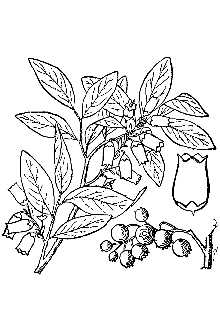
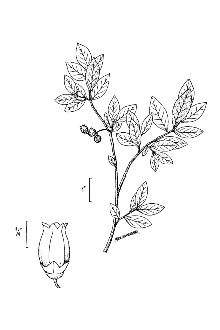
Botany Dept., NMNH, Smithsonian Institution @ PLANTS General: Heath family (Ericaceae). Native shrubs 2-3(-4) meters tall, crown-forming, forming dense colonies, the twigs warty and yellow-green, glabrous. Leaves deciduous, alternate, simple, narrow to broadly elliptic or ovate, 3.8-8.2 cm long, pubescent at least on the veins beneath, slightly waxy above, the edges smooth and ciliate to toothed. Flowers 8-10 in a cluster, 6-12 mm long, urn-shaped, white, with 5 petals. Fruits berries are 5-12 mm wide, blue to blue-black and many-seeded. The common name refers to the relatively tall stature of these plants. Variation within the species: The highbush blueberry complex is highly variable and includes diploids, tetraploids, hexaploids, and various hybrid combinations. Recent studies (Vander Kloet in 1980 and 1988) have recommended treating the complex very broadly, using only the single name V. corymbosum, but not all authors have accepted that (for example, see Uttall 1986, 1987). As treated in the PLANTS database, the complex includes a group of interrelated species that have generally been recognized as “highbush” blueberries – these species* (or hybrids), with synonyms, are listed below. * Vaccinium X atlanticum Bicknell * Vaccinium corymbosum L. synonym: Vaccinium constablaei Gray * Vaccinium formosum Andr. synonym: Vaccinium australe Small * Vaccinium fuscatum Ait. synonym: Vaccinium arkansanum Ashe synonym Vaccinium atrococcum (Gray) Heller synonym Vaccinium fuscatum Aiton *Vaccinium simulatum Small *Vaccinium virgatum Ait. synonym: Vaccinium amoenum Aiton synonym: Vaccinium ashei Reade Highbush blueberry (V. corymbosum) hybridizes with one of the “lowbush” blueberries (V. angustifolium Ait.). Hybrids used in commercial fruit production are V. corymbosum X V. darrowi (southern highbush blueberry), (V. arboreum X V. darrowi) x V. corymbosum (pollen donor), and southern highbush blueberry hybrids X V. simulatum. Distribution: Widespread in eastern North America, from Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec, and Ontario, Maine to Wisconsin, southward to South Carolina and Georgia and along the Gulf coast to Arkansas, Louisiana, east Texas, and Oklahoma. It has been introduced outside of its natural range for commercial berry production in Wisconsin, Washington, British Columbia, and New Brunswick. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site.
Adaptation
Highbush blueberry grows best and most commonly in moist or wet peat of moderate to high acidity – in and around marshes, swamps, and lakes, often with extended flooding, as well as on floodplains, sheltered slopes, and ravines. It also occurs in drier areas – dunes and barrier beaches, rocky hillsides, oak woods, and pine woods. It occurs as a dominant or co-dominant on Appalachian "heath balds." All of these are more or less open sites, and because of its shade intolerance, highbush blueberry can be eliminated as shading increases with overstory cover. Flowering (February-)March-June, sporadically in the southern portion of its range; fruiting (April-)May-October, about 62 days after flowering.
Establishment
Highbush blueberry produces abundant fruit every year. Bees are the primary pollinator. The seeds may be widely dispersed in bird and mammal droppings, but germination success can be reduced up to 15% after passing through an animal gut. In the southern portion of its range, highbush blueberry seeds have thick seed coats and require cold stratification before germination. Those from northern regions produce thinner seed coats and germinate in the autumn after dispersal. Some reports describe vigorous sprouting from the root-crown in highbush blueberry after top-kill by fire or disturbance, while others note that sprouting is uncommon. This perhaps reflects the variability (and perhaps the taxonomic uncertainty) that exists within the species complex. Plants also have been noted to occasionally produce root sprouts 1-2 meters away from the parent.
Management
Seeds or cuttings can propagate plants of highbush blueberry. Ideal soil for cultivation is moist, high in organic matter, highly acidic (4.5-5.5), and well drained. The plants grow in full sun to partial shade, but those in open sites produce more flowers and have brighter fall foliage color. Highbush blueberry (V. corymbosum) is self-fertile, but cross-pollination increases fruit set and results in larger, earlier berries with more seeds (see Agriculture Western Australia 2000). Other species of the complex are partially or completely self-incompatible. Cultivars, Improved and Selected Materials (and area of origin) These plant materials are readily available from commercial sources. Contact your local Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources
Conservation
Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”
References
Agriculture Western Australia 2000, Bee pollination benefits for blueberry crops, Web site, <http://www,agric,wa,gov,au/programs/dairy/apiculture/blueberry,htm#ref10> Camp, W,H, 1945, The North American blueberries with notes on other groups of Vacciniaceae, Brittonia 5:203-275, Garrison, N, 1998, Descriptions of blueberry varieties in trial conducted by Nancy Garrison, Master Gardeners of Santa Clara County Online, Univ, of California Cooperative Extension, Urban Horticulture Program, <http://www,mastergardeners,org/recommend/bluevar,html> Reiger, M, 2000, Mark’s fruit crops, Univ, of Georgia, Dept, of Horticulture, Web site, <http://www,uga,edu/hortcrop/rieger/index,html> Uchytil, R, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Cyanococcus corymbosus (L.) Rydb..,J, 1993, Vaccinium corymbosum, IN: W,C, Fischer (compiler), The fire effects information system [Data base], U,S,D,A,, Forest Service, Intermountain Research Station, Intermountain Fire Sciences Laboratory, Missoula, Montana, <http://www,fs,fed,us/database/feis/> Uttal, L,J, 1986, Updating the genus Vaccinium (Ericaceae) in West Virginia, Castanea 51:197-201, Uttal, L,J, 1987, The genus Vaccinium L, (Ericaceae) in Virginia, Castanea 52:231-255, Vander Kloet, S,P, 1980, The taxonomy of the highbush blueberry, Vaccinium corymbosum, Canad, J, Bot, 58:1187-1201, Vander Kloet, S,P, 1988, The genus Vaccinium in North America, Research Branch, Agriculture Canada, Publ, 1828,
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
Northern highbush blueberry, southeastern highbush blueberry, Maryland highbush blueberry, black highbush blueberry, American blueberry, New Jersey blueberry, rabbiteye blueberry, swamp blueberry, tall huckleberry, mayberry, whortleberry
Uses
Fruit production: V. corymbosum, highbush blueberry, a native North American shrub cultivated throughout the country, is the major blueberry-producing species in commerce. More than 50 cultivars have been developed, primarily for commercially valuable fruit characteristics and seasonality. Landscaping: A few selections are used in landscaping, especially as plantings in wet areas or to attract wildlife. Food: Highbush blueberries are eaten raw, smoke-dried, sun-dried, boiled, and baked in a wide variety of culinary settings. They have one of the highest concentrations of iron of the temperate fruits. Wildlife: Blueberries provide important summer and early fall food for numerous species of game birds, songbirds, and mammals.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, and wetland indicator values).
Description
Botany Dept., NMNH, Smithsonian Institution @ PLANTS Highbush blueberry is a native, upright, 6-12 feet tall, crown-forming shrub. The common name refers to the relatively tall stature of these plants. Twigs are yellow-green (reddish in winter) and covered with small wart-like dots. Leaves are deciduous, alternate, simple, elliptic or ovate, 1 to 3½ inches long and slightly waxy above with pubescence (hairs) at least on the veins beneath. The white or pink-tinged flowers are small and urn-shaped with 5 petals, and occur 8 to 10 per cluster. Flowering occurs February to June, sporadically in the southern portion of its range; fruiting occurs April to October, about 62 days after flowering. Fruits are ¼ - ½” blue-black berries with many seeds. In the PLANTS database, plants known as “highbush” blueberries are actually a group of interrelated species. Hybrids are often used in commercial fruit production.
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution
Distribution
Widespread in eastern North America, the highbush blueberry has been introduced outside of its natural range for commercial berry production. The most common native habitat is in moist or wet peat of moderate to high acidity – in and around marshes, swamps, lakes and flood-prone areas. V. corymbosum also occurs in drier areas such as dunes and barrier beaches, rocky hillsides, oak woods, and pinewoods. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website.
Establishment
Highbush blueberry produces abundant fruit every year. Highbush blueberry (V. corymbosum) is self-fertile, but cross-pollination increases fruit set and results in larger, earlier berries with more seeds (Agriculture Western Australia 2000). Other species of the complex are partially or completely self-incompatible. Bees are the primary pollinators. The seeds may be widely dispersed by birds and mammals, but germination can be reduced up to 15% after passing through an animal gut. In the southern portion of its range, highbush blueberry seeds have thick seed coats and require cold stratification before germination. Those from northern regions produce thinner seed coats and germinate in the autumn after dispersal. Plants of highbush blueberry can be propagated by seeds or cuttings. Occasionally sprouting has occurred from root-crowns after top kill by fire or disturbance. Plants have also been noted to produce root sprouts that emerge 1-2 meters away from the parent plant.
Management
Ideal soil for cultivation is moist, high in organic matter, highly acidic (4.5-5.5), and well-drained. The plants grow in full sun to partial shade, but those in open sites produce more flowers and have brighter fall foliage color.
Pests and Potential Problems
Insects, diseases and wildlife pests need to be controlled in commercial production, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Cyanococcus corymbosus (L.) Rydb.., Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) Improved varieties for commercial berry production are readily available, Non-selected materials for conservation use are also available from nurseries, Prepared By: Guy Nesom Formerly BONAP, North Carolina Botanical Garden, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina Kathy Davis USDA NRCS National Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, Maryland
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -33 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 100 |
| Hedge Tolerance | Low |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.7 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1700 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 1200 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 50 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 32 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Salinity Tolerance | High |
| Shade Tolerance | Tolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | White |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Moderate |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 12.0 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 12 |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Blue |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Low |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Summer |
| Seed per Pound | 975000 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Early Summer |
| Propagated by Cuttings | Yes |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | Yes |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Medium |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | Yes |