Bignonia radicans L.
Scientific Name: Bignonia radicans L.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | BIRA2 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Vine |
| Native Locations | BIRA2 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Bignonia radicans, cow-itch, Gelseminum radicans, Tecoma radicans, Tecoma speciosa, trumpet flower, trumpet vine, , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Bignonia radicans L..
Uses
Ornamental: The showy flowers of trumpet creeper make this plant appropriate for some gardening and landscaping needs. It is often used as a cover for fences, arbors, walls, pillars or large trellises and as a groundcover. The cigar-like fruit may be considered decorative during winter. Wildlife: The tubular flowers and large quantities of nectar produced by trumpet creeper are attractants for hummingbirds and butterflies. The vines also provide habitat to ants.
Legal Status
Status
Status
Trumpet creeper is an invasive weed. Please consult the PLANTS Web site (http://plants.usda.gov) and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Weediness
This plant may become weedy or invasive in some regions or habitats and may displace desirable vegetation if not properly managed. Please consult with your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, or state natural resource or agriculture department regarding its status and use. Weed information is also available from the PLANTS Web site at plants.usda.gov. J.R. Manhart. 2004 Texas A & M University Herbarium
Description
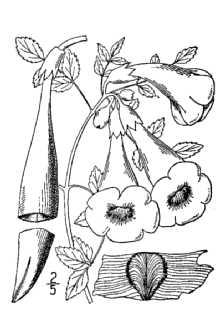
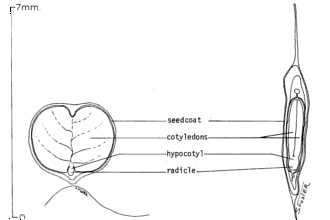
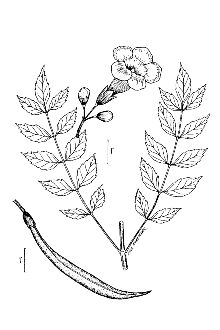
General: Bignonia Family (Bignoniaceae). Trumpet creeper is a deciduous or partly evergreen vine that climbs by aerial rootlets and twining stems. This is a U.S. native. Stems can grow up to 12 m long and have numerous aerial rootlets. Leaves are opposite, pinnately compound and coarsely toothed, composed of 7, 9, or 11 leaflets. Leaflets are somewhat shiny and dark green. Flowers are yellow-orange to red, tubular, and up to 8 cm long and 4 cm wide at the mouth. Flowers are born in clusters of four to a dozen and bloom from July through August. The fruit is a flat, tapered capsule, 8-13 cm long with seeds that are flat and winged. Distinguishing characters of trumpet creeper include its U-shaped bundle scars on the stem, abundant root-like aerial stems, opposite compound leaves that are coarsely toothed, large trumpet-shaped flowers, and its light tan bark that appears flaky on mature stems. Distribution: Trumpet creeper is native to eastern, north-central, and south-central portions of the United States and has become naturalized in New England. Its natural range occurs from New Jersey to Ontario and Iowa, and south to Florida and Texas. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Trumpet creeper is found in thickets, dry woods, waste grounds, railroads, disturbed sites, clearings, and along roadsides and fencerows.
Adaptation
The USDA hardiness zones for trumpet creeper are 4-10. It grows in wet to dry soils and sand, loam, or clay soil types with a pH range of 3.7 to 6.8. Trumpet creeper prefers full sun for best flowering.
Management
If not controlled, rampant growth will become a problem. Vines should be thinned throughout the growing season and cut back in winter to prevent aggressive spread.
Pests and Potential Problems
Planthoppers may occasionally feed on trumpet vine but generally do not cause serious damage. Leaf spots caused by various fungi may be seen but are not serious. Mildew causes a white powdery growth on the leaves.
Seeds and Plant Production
Plant Production
Plant Production
Trumpet creeper is typically propagated by cuttings. It readily roots and develops new suckers that allow the species to grow rapidly. Seeds are prepared for germination by stratifying them in moist sand for 60 days at 4oC and 30% relative humidity. Fungicide should be added to the sand to prevent mildew formation. For spring outplanting, seeds are sown in early fall. Sixty percent germination will occur within two weeks of removal from stratification conditions. There is no special treatment required for establishment other than monitoring for water needs. During the active growth phase, plants will need to be cutback to encourage root growth and prevent the tangling of foliage. Seedlings will need to harden in winter-like temperatures before outplanting. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) The NRCS Plant Materials Program has not released any cultivars of trumpet creeper for conservation use. Contact your local Natural Resources
Conservation
Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government.” The Natural Resources Conservation Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.” Ornamental cultivars of trumpet creeper include ‘Atropurpurea,’ ‘Crimson Trumpet,’ ‘Flamenco,’ ‘Flava,’ ‘Madame Galen,’ ‘Minor,’ ‘Praecox,’ ‘Speciosa,’ and ‘Variegata.’ These cultivars have been bred for flower and foliage color and for rapid growth.
Control
Please contact your local agricultural extension specialist or county weed specialist to learn what works best in your area and how to use it safely.
References
Brand, M. 2001. University of Connecticut plants database, (http://www.hort.uconn.edu/plants/index.html, 30 April 2004). University of Connecticut, Storrs. Davis, K.M. and J.L. Kujawski. 2001.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -13 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 165 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| pH, Maximum | 6.8 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.9 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 1700 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 1200 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 32 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 14 |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| Bloat | None |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Shape and Orientation | Climbing |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Red |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 2.0 |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Form | Single Crown |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed per Pound | 136000 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Summer |
| Propagated by Cuttings | Yes |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |