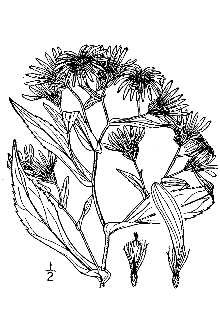
Aster prenanthoides Muhl. ex Willd.
Scientific Name: Aster prenanthoides Muhl. ex Willd.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | ASPR4 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Forb/herb |
| Native Locations | ASPR4 |
Plant Guide
Use a soil moisture meter to monitor the soil moisture where Aster prenanthoides Muhl. ex Willd. is planted.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
Crooked stem aster Zigzag aster Aster prenanthoides L.
Uses
Crooked stem aster is an adaptable, easy to grow ground cover for dry, sunny locations, It is a native plant and can be part of a good wildlife seed mixture where native grasses and wildflowers are seeded together, Ethno botanical: A tea made from the roots of crooked-stem aster has been used to treat fevers in babies and colds and kidney ailments in adults, Landscaping and wildlife: Crooked-stem aster creates showy mounds of blooms in summer and is excellent for native landscape gardens, Asters will grow on disturbed sites and can be used for wildlife habitat restoration, Crooked stem aster is attractive to pollinators, including long-tongued bees, short-tongued bees, small to medium-sized butterflies, and skippers, Many kinds of insects feed on the foliage and other parts of asters, including the caterpillars of the butterfly Chlosyne nycteis (Silvery Checkerspot) and many moth species, Wild Turkey, other upland game birds and mammalian herbivores occasionally eat the seeds and foliage of asters, even though their food value is low, , Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Aster prenanthoides Muhl. ex Willd..
Status
Crooked-stem aster is listed as a special concern in Connecticut and as threatened in Massachusetts. Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description and Adaptation
Adaptation
Adaptation
Crooked-stem aster is a native, perennial wildflower that grows from 1 – 4 feet tall. The aster’s rigid stems are much-branched from the base. The leaves are .5 – 3 inches long, simple (not made up of multiple leaflets), and alternate (progressing singly up the stem). The flowers are fragrant with approximately 30 blue ray florets per flower. The disk florets are yellow and the bracts are glandular with long, green, loose or spreading tips. Flowers appear in summer and give way to flat, brown, hairy achenes (dry fruits). Crooked-stem aster spreads through stolons (horizontal stems that produce new plants from buds). Distribution: Crooked-stem aster grows in moist, loamy soils, full sun to partial shade in riparian and forest edge habitats. It is distributed from Ontario south to North Carolina and Tennessee (USDA cold hardiness zones 4 – 7).
Establishment
Seed propagation Seeds can be collected from wild plants in the fall when the seed separate easily from the stems that attached them to the flower. Seeds should be collected in paper bags and allowed to dry for 1–2 weeks. If seeds are sown directly, sow them five-eighths of an inch deep in the fall and sow thickly. Plant a cover crop of a cool-season annual grass over the seedbed to protect seed over the winter. If seeds are to be propagated in a container, they should be stored for 1–3 months at 30–40 degrees Fahrenheit before sowing. Many species of Aster benefit from moisture during the cold storage (stratification) period. Use a perlite/vermiculite mix for stratification. The seed will germinate in 10 to 15 days at 72 degrees Fahrenheit. Germination to true leaf stage is 7 to 15 days. Seedlings are thinned at this stage. Vegetative propagation Propagate by softwood cuttings taken in late spring.
Management
Crooked-stem aster colonizes by horizontal stems which grow at the soil surface, so thin it regularly to control its spread. Crooked-stem aster may open up if it becomes too top-heavy, so prune it back by no more than half in mid-June to keep it thick. After it goes dormant in late fall or early winter cut it back to the round level ring of leaves at the plants base. Crooked-stem aster prefers neutral to slightly acidic soils.
Pests and Potential Problems
Crooked stem aster is susceptible to many leaf spots, rusts and mildews which will affect the lower leaves but usually do no permanent damage. The most destructive diseases in the cultivation of asters are various forms of stem-rot. They are of fungus origin and are induced by allowing the plants to remain moist for an extended period of time. The infection usually takes place in the seed-row, but often no effect is noticed until the plants are nearly full-grown, when they suddenly wilt and die. The “yellow disease” causes the plants to have a bleached appearance and to make a spindling growth. Thorough cultivation of the soil is the best preventive.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -38 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Medium |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 100 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 7.2 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.5 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 11000 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 2700 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 50 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 10 |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Active Growth Period | Spring, Summer, Fall |
| Bloat | None |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Blue |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Short |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 4.0 |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Rhizomatous |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Moderate |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Low |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Seed per Pound | 700000 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | Medium |
| Commercial Availability | No Known Source |
| Bloom Period | Summer |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |