American Beautyberry
Scientific Name: Callicarpa americana L.

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | CAAM2 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Shrub |
| Native Locations | CAAM2 |
Plant Guide
Uses
Ethnobotanic: The roots, leaves and branches of the American beautyberry were used by the Alabama, Choctaw, Creek, Koasati, Seminole and other Native American tribes for various medicinal purposes, The roots, leaves and branches were made into a decoction that was used in sweat baths to treat both malarial fevers and rheumatism, The boiled plant parts were poured into a big pan that was placed near the patient inside a sweathouse, A similar decoction of the roots was used to treat dizziness and stomachaches, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of American Beautyberry., The roots of Callicarpa americana were boiled with roots from Rubus spp, to make an infusion to treat dysentery, The roots and berries were boiled and drunk to treat colic, The bark from the stems and roots was used to treat itchy skin, A tea from the root bark was taken to treat urine retention or “urine stopped-up sickness,” Wildlife: The fruits of American beautyberry are an important food source for many species of birds including bobwhite quails, mockingbirds, robins, towhees, and brown thrashers, Animals that eat the fruit include armadillos, raccoons, wood rats, gray foxes, opossums, and white-tailed deer, The long-lasting fruits provide food for birds and animals well into the winter months when other food-sources are unavailable, Other: Beautyberry shrubs are raised for their ornamental flowers as well as their colorful clusters of fruits,
Status
© William S. Justice @ PLANTS Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
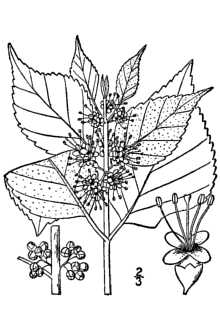
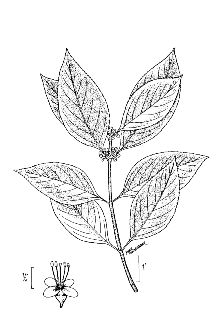
General: Vervain Family (Verbenaceae). American beautyberry is a native, perennial shrub. These small, deciduous shrubs reach from 1 to 2 m in height. The leaves are opposite, elliptical to ovate in shape (7 to 15 cm long) and have saw-toothed margins. The under-side of the leaves can be covered with white or rust-colored woolly hairs. The inconspicuous blue, violet, pink, or white flowers are borne in axillary clusters that bloom from late spring to early summer. The flowers are funnel-shaped with four clefs. The round, showy, violet or magenta drupes or fruits are 4-5 mm in diameter. The very juicy fruits, containing from 2 to 4 seeds, begin to ripen in August or September. These colorful fruits remain on the shrubs long after the leaves drop. Distribution: For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: American beautyberry shrubs occur in dry open woods, moist woods, thickets and hammocks. They occur as understudy species in upland pine forests, upper slope pine-oak forests and old-growth maritime forests. These shrubs are adapted to climates with hot, humid summers and moderate winters.
Establishment
These shrubs may be propagated by softwood cuttings, but they are primarily grown from seed. The seeds do not require pretreatment for germination. The many volunteers that this plant produces are very hearty and can be dug up and transplanted elsewhere in a more desirable location. The plants do well in partial shade and sunny locations in well-drained soils. The shrubs have a denser habit and produce more fruit in sunny locations.
Management
This plant can produce abundant volunteers from the many seeds that drop to the soil. The flowers are produced on new growth, so prune plants after the fruits are gone to increase the next year’s growth and berry production. The plants can take a hard pruning and may be pruned to the ground level in the winter if desired. Cultivars, Improved and Selected Materials (and area of origin) These plant materials are somewhat available from commercial sources. The white-fruited C. Americana var. lacteal is available from specialty nurseries. Contact your local Natural Resources
Conservation
Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) office for more information. Look in the phone book under ”United States Government”. The Natural Resources Conservation Service will be listed under the subheading “Department of Agriculture.”
References
Bailey, L.H. & E.Z. Bailey 1976. Hortus Third: A concise dictionary of plants cultivated in the United States and Canada. Simon and Schuster Macmillan Co., New York, New York. 1290 pp. Barbour, M.G., & W.D. Billings, Editors 2000. North American terrestrial vegetation, Second Edition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom. 708 pp. Chapman, A.W. 1883. Flora of the southern United States: Flowering plants and ferns. Second Edition. J. Wilson and Son, Cambridge, Massachusetts. 698 pp. Dirr, M.A. 1997. Dirr’s hardy trees and shrubs: an illustrated encyclopedia. Timber Press, Portland, Oregon. 493 pp. Dirr, M.A. 1998. Manual of woody landscape plants. Fifth Edition. Stipes Publishing, Champaign, Illinois. 1187 pp. Greene, W.F. & H.L. Blomquist 1953. Flowers of the south: Native and exotic. University of North Carolina Press. Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 208 pp. Martin, A.C., H.S. Zim & A.L. Nelson 1951. American wildlife and plants: A guide to wildlife food habits. Dover Publications, New York. 500 pp. Moerman, D.E. 1998. Native American ethnobotany. Timber Press, Portland, Oregon. 927 pp. Moerman, D.E. 1999. Native American
Ethnobotany
Database: Foods, drugs, dyes and fibers of native North American peoples. The University of Michigan-Dearborn. [Online]. Available: http://www.umd.umich.edu/cgi-bin/herb(19 June 2001) Ottensen, C. 1995. The native plant primer. Harmony Books, New York, New York. 354 pp. Rogers, D.J. & C. Rogers 1991. Woody ornamentals for Deep South gardens. University of West Florida Press, Pensacola, Florida. 296 pp. Small, J.K. 1933. Manual of Southeastern flora. University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1554 pp. Smith, A.I. 1979. A guide to wildflowers of the Mid-south. Memphis State University Press, Memphis, Tennessee. 281 pp. Sturtevant, W.C. 1954. The Mikasuki Seminole: medical beliefs and practices. Doctoral Dissertation, Yale University. 538 pp. Swanson, R.E. 1994. A field guide to the trees and shrubs of the Southern Appalachians. John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland. 399 pp. Swanton, J.R. 2000. Creek religion and medicine. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, Nebraska. 684 pp. Taylor, L.A. 1940. Plants used as curatives by certain Southeastern Tribes. Botanical Museum of Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts. 88 pp. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory 2001. Fire effects information system, [Online]. Available: http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/. [19 June 2001]. Young, J.A. & C.G. Young 1992. Seeds of woody plants in North America. Dioscorides Press, Portland, Oregon. 407 pp.
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
American beautyberry is also known as French mulberry, sourbush, bunchberry, or purple beauty-berry. In Greek, the genus name Callicarpa means callos, “beauty” and carpos “fruit”.
Uses
Ethnobotanic: The roots, leaves, and branches were used by various Native American tribes for medicinal purposes to treat malarial fevers and rheumatism. The roots were used to treat dizziness, stomachaches and dysentery. Roots and berries were boiled and drunk to treat colic. In the early 20th century, farmers would crush the leaves and place them under the harnesses of horses and mules to repel mosquitoes. The farmers rubbed the crushed leaves on themselves to repel mosquitoes and biting bugs. Studies conducted by the Agricultural Research Service has shown two compounds – callicarpenal and intermedeol - are responsible for the repellant. Wildlife: The fruit is high in moisture content and is an important food source for more than forty species of songbirds including the American Robin, Brown Thrasher, Purple Finch, and Eastern Towhee. The drupes or clusters are eaten by armadillo, foxes, opossum, raccoon and squirrels. White tailed deer consume the fruit in the fall after leaf drop. They also browse the leaves in summer when highly preferred foods are not available. Protein content of the leaves ranges from 18 percent in spring to 8 percent in fall. Other: American beautyberry is used as an ornamental shrub in mass plantings, borders and container planting. Livestock: Cattle browse the twigs in winter and the leaves and twigs in the spring.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site; http://plants.usda.gov and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g., threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description and Adaptation
Adaptation
Adaptation
American beautyberry is a fast growing native perennial shrub; growing five to eight feet tall and almost as wide with drooping branches. The elliptical to ovate shaped leaves have an opposite arrangement with saw toothed margins. The underside of the leaves may be covered with wooly like hairs. The stems are slender, gray to reddish brown, and terete or four sided. In late spring to early summer, inconspicuous flowers of blue, violet, pink, or white are arranged in clusters on the stems between the leaves. In August or September, clusters of small purple to blue berries or drupes encircle the woody stems. Each small berry in the cluster contains two to four seeds about 1/16 in. long. This plant is distributed throughout the southeastern United States from Texas and Oklahoma east to Maryland. It also grows in the Caribbean and northern Mexico. American beautyberry is found in woods, particularly on moist areas under open pine canopies, thickets, right of ways, and fence rows. It is adapted to moist, loam, sandy or shallow upland sites and a wide pH range. The shrub is considered a pioneer species and is characteristic of the mid stages of plant succession. This plant is very tolerant of fire. However, it is intolerant of deep shade and declines in number when mid-story vegetation is dense.
Establishment
American beautyberry can be propagated by transplanting volunteer plants, softwood cuttings, or seeds, Volunteer plants are very hearty and can be dug up and transplanted to a different location, Softwood stem cuttings (4” to 6” long) can be taken in the summer and fall, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of American Beautyberry., Dip the cut end into indol -3 – butyric acid (IBA; 1000 ppm) and insert into a rooting media, Keep the temperature of the media between 70-750, Water the cuttings and cover with plastic to keep the material moist, Roots should develop within a few weeks, After rooting begins, remove the plastic at longer intervals each day for seven to ten days, Afterwards, remove the plastic permanently, The seed is easily gathered by hand picking the mature fruit in the fall, The harvested berries, which contain 2 to 4 seeds each, can be treated in several ways; one is planting the berries in the fall for spring germination, American beautyberry seeds can survive several years in the soil bank, Another way is cleaning the seeds using a kitchen blender for small seedlots, Mix the berries with at least five times their volume of water and pour into the blender, Run the blender at its lowest speed using short bursts of a few seconds at a time to separate the skin and tissue from the seeds, Eventually, mature seeds sink to the bottom, while immature seeds, skins and tissue remain near the top, Check the seeds for possible damage, Pour off the unwanted material and repeat the process two or three times, Eventually, a clean seed sample will be left at the bottom of the blender, Drain the seeds and spread them out to dry, After drying, the seeds are ready for planting or storage in a cool, dry place,
Management
Prune the plants in the fall or winter to maintain its form. Cut away the old stems since the berries are present only on new growth.
Pests and Potential Problems
Some of the diseases which affect this genus include leaf spots (Atractilina callicarpae) and black mold (Meliola cookeana).
Environmental Concerns
American beautyberry seed is dispersed by birds and animals. Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) This plant is available from commercial sources. Some nurseries produce a white fruited plant; C. Americana var. lactea. . Prepared By: Melinda Brakie, USDA NRCS Plant Materials Center, Nacogdoches, Texas.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
|---|---|
| Hedge Tolerance | Medium |
| Hedge Tolerance | Medium |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 200 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 175 |
| Fire Tolerance | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | High |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | 2 |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Medium |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Medium |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | None |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -8 |
| Shade Tolerance | Tolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intermediate |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 14 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 35 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 2700 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 1200 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 4800 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 2700 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.8 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.8 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.2 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.0 |
| Moisture Use | High |
Morphology/Physiology
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Shape and Orientation | Semi-Erect |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Foliage Texture | Medium |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Flower Color | White |
| Flower Color | Blue |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fall Conspicuous | Yes |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| C:N Ratio | High |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Active Growth Period | Spring and Summer |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Purple |
| Resprout Ability | Yes |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 6.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 9.0 |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Purple |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | Yes |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Growth Form | Multiple Stem |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 6 |
| Height at 20 Years, Maximum (fee | 9 |
Reproduction
| Propagated by Cuttings | Yes |
|---|---|
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Seed per Pound | 85000 |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Seed per Pound | 85000 |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Bloom Period | Early Summer |
| Bloom Period | Early Summer |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Propagated by Bare Root | Yes |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Container | Yes |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | Yes |
Suitability/Use
| Palatable Browse Animal | Medium |
|---|---|
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Low |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | High |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |