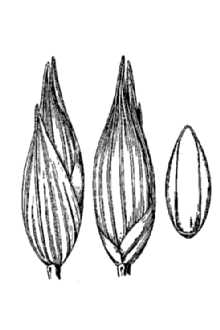
Bitter Panicgrass
Scientific Name: Panicum amarum Elliott

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | PAAM2 |
| Group | Monocot |
| Life Cycle | Perennial |
| Growth Habits | Graminoid |
| Native Locations | PAAM2 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Bitter panicgrass, bitter beachgrass, coastal panicgrass, Chasea amara (Elliott) Nieuwl., Panicum amaroides Scribn. & Merr., Panicum amarulum (Hitchc. & Chase) P.G. Palmer, Panicum amarum Elliot var. minor Vasey. Varieties include P. amarum Ell. var. amarulum and P. amarum Ell. var. amarum.
Uses
Erosion control: The principal use for bitter panicum is in coastal dune erosion control, however it may have a role in stabilizing other dry, sterile areas such as roadsides and minespoils. Bitter panicum is recommended for beach dune enhancement and stabilization on coastal beaches and barrier islands. It is an ideal dune plant. The above ground portion of the plant reduces wind velocity allowing sand to drop out of the wind stream and accumulate. The below ground portion of the plant stabilizes and holds the sand in place with an extensive fibrous root and rhizome system. Livestock and forage: Bitter panicum is consumed by cattle, sheep, and goats. This grass has a low-medium browse and grazing palatability and a medium protein potential. It is a favorite forage of livestock in some areas and was eliminated along some portions of the Texas barrier islands by grazing. When livestock are removed, this grass reestablishes rapidly. Ethnobotanic: A warm infusion of Panicum sp. (panicgrass) leaves was taken by the Creek Indians for fevers, especially those caused by malaria. It was also used for ‘rabbit sickness’, muscular cramps, cough, dry throat, noisy chest and as a bath for ‘gopher-tortoise sickness’ by the Mikasuki Seminole. Stems were used for padding the inside of Cherokee moccasins. Wildlife Use: Bitter panicum can provide cover and/or habitat for song birds, water fowl and small mammals.
Status
This plant is listed as Threatened in Connecticut with state protection status. Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for changes on this plant’s current status (e.g. threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Description
General: Grass Family (Poaceae). Bitter panicum is a native, perennial, rhizomatous, warm-season grass growing to a height of 4-8 feet with a growth habit ranging from erect to prostrate to decumbent. The leaves are 1/4 to 1/2 inch wide, 7 to 20 inches long, smooth without hair, and bluish in color. A robust grass, it spreads slowly from short, strong rhizomes or by rooting from lower nodes of plant stems (culms) to form open clumps. The inflorescence is a narrow panicle 12 to 15 inches in length that is contracted in maturity. Flowering begins in September and continues through December. Bitter panicum is a hexaploid (2n=54), consequently, seeds are consistently sterile. Small quantities of poor quality seed are produced on compact clusters 6 to 12 inches long and 2 to 4 inches wide. Reproduction is vegetative by lateral tillering from established plants. Plants can spread from an aggressive, scattered system of rhizomes, but the stands are rather open. Distribution: The native range and distribution of bitter panicum is along the coastal beach system of the north central Gulf of Mexico basin. It is also distributed throughout the East and lower Midwest; it can be found along the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico from Connecticut to northeastern Mexico. It is also found as an introduction in a few inland locations in New Mexico, North Carolina, and West Virginia, as well as in the Bahamas and Cuba. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Bitter panicum grows on coastal dunes, in interdunal swales, overwash sands, wet sandy soils, low fertility soils, and the margins of swamps. On coastal dunes, it is most likely found in the lower foredune slopes of the frontal zone, which is closest to the ocean and supports mainly grasses and other herbaceous plants tolerant of exposure to salt spray. It also occurs on dune crests, as well as in the backshore area near dunes and on both the leeward and the windward slopes of dunes or dune ridges. It favors exposed areas where windblown sand accumulates. In the southeastern U.S., bitter panicum is equally likely to occur in wetlands or non-wetlands (estimated probability 34%-66%). In the northeast and the southern plains it usually occurs in non-wetlands (estimated probability 67%-99%), and is only occasionally found on wetlands (estimated probability 1%-33%).
Adaptation
Bitter panicum is an early colonizing species that can tolerate the harsh environment of the dune system which is subject to salt spray, storm surges, occasional inundation, high temperatures, low soil moisture and fertility, sand abrasion, and smothering by drifting sand. It is adapted to very dry, sterile sites and can flourish on fertile, well drained soils. It is better adapted for transplanting than seaoats (Uniola paniculata). In areas of heavy sand accumulation, only a small fraction of the entire plant may be exposed. It can withstand periods of extended drought and is somewhat winter hardy. Year long growth can occur where sand is actively accumulating, but winter cover is sparser. This grass does not perform well in shade and prefers a soil pH of 5.0-7.5.
Plant Production
Bitter panicum is established from container grown or bare root plant materials. Most any plant container size can be used successfully. Propagation for container production is accomplished by plant divisions or cuttings. Rhizomes or stem nodes are used for cuttings. Sand to sandy loam potting medium is preferred, however, sand peat mix or other prepared soil mixes can be used successfully. When propagating from stem cuttings, prepare stem sections with two nodes per cutting. Cuttings are placed vertically in the container with both nodes buried in the medium.
Establishment
Generally, no site preparation is required when planting bitter panicum. Freshly dug bareroot shoots (tillers) and rooted or unrooted stem cuttings can be used in plantings. Container grown plants have been proven to be more reliable in establishing stands. Field plantings are established by planting on 2 to 5 feet centers between plants. Spacing is dependent on the protective cover desired, but a 2 foot spacing is frequently used. Place plants 8 to 10 inches deep or deeper in moist soil. Bury unrooted stems end to end in trenches 4 to 6 inches deep and 2 to 3 feet apart leaving the top 6 to 10 inches of the stem exposed. Unrooted cuttings can also be planted 3 to a hole. Bitter panicum can be established in the fall with rooted cuttings. It can be planted in late winter or early spring, although success has been noted when planting young tillers in late spring, if a rainy season is more likely to occur then, as in some regions of distribution. Containerized plants can be planted year around if moisture is adequate; however, better establishment may be achieved by planting in late winter or early spring. This grass can grow on low fertility soils, however, if fertilization is desired place a slow release tablet with each plant while planting or broadcast a balanced fertilizer such as 13-13-13 after planting.
Management
During establishment, restrict traffic and livestock grazing. All sites should be allowed to establish the first year, prior to any grazing. Once grazing is started, do not graze lower than 4 to 6 inches. Apply fertilizer according to soil test recommendations. Application of fertilizer may be split. Bitter panicum has a high fire tolerance, making it tolerable to controlled burns.
Pests and Potential Problems
There are no known serious pests of bitter panicum.
Environmental Concerns
Concerns
Concerns
There are no known serious environmental concerns, Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) ‘Fourchon’ originated from a native stand of bitter panicum found growing on a coastal beach in Lafourche Parish, Louisiana, It was selected for its vigorous growth, persistence after storm events, and performance in stabilizing dunes enhanced or created with sand fencing structures, Fourchon bitter panicum has been tested and has proven performance in plantings on coastal beaches of Mississippi and Louisiana, For more information on the availability and use of Fourchon bitter panicum, contact the Natural Resources Conservation Service, Golden Meadow Plant Materials Center, Other cultivars include ‘Northpa’ (NC) and ‘Southpa’ (FL) both of which have a vigorous rhizomatous growth habit and rapid spread rate, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Bitter Panicgrass., Plant materials are available from commercial sources,
Fact Sheet
Alternate Names
bitter panicgrass
Uses
Erosion control: The principal use for bitter panicum is in coastal dune erosion control and it may have a role in stabilizing other dry, sterile areas such as roadsides and minespoils. Livestock: Bitter panicum is consumed by cattle, sheep, and goats.
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Bitter Panicgrass.,g, threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values),
Description
Panicum amarum Ell., bitter panicum, is a perennial, U.S. native, warm season grass growing to a height of 7 feet with a growth habit ranging from erect to prostrate. The leaves are 1/4 to 1/2 inch wide, 7 to 20 inches long, smooth without hair, and bluish in color. A robust grass, it spreads slowly from short, strong rhizomes to form open clumps. Small quantities of poor quality seed are produced on compact clusters 6 to 12 inches long and 2 to 4 inches wide.
Adaptation and Distribution
Distribution
Distribution
Bitter panicum is adapted to very dry sterile sites. It can withstand periods of extended drought and is somewhat winter hardy. Bitter panicum is distributed throughout the East and lower Midwest. For a current distribution map, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Website.
Establishment
Generally, no site preparation is required when planting bitter panicum. Freshly dug bareroot shoots (tillers) and rooted or unrooted stem cuttings can be used to establish plantings. Plant potted plants and bare root plants in staggered rows 2 to 3 feet apart with plants 2 feet apart in each row. Place plants 8 to 10 inches deep or deeper in moist soil. Bury unrooted stems end to end in trenches 4 to 6 inches deep and 2 to 3 feet apart leaving the top 6 to 10 inches of the stem exposed. Plant unrooted cuttings 3 to a hole in staggered rows 2 to 3 feet apart with holes 2 feet apart in each row. USDA NRCS National Plant Materials Center Beltsville, MD Bitter panicum can be established in the fall with cuttings, in late winter or early spring with potted plants, or in late spring (beginning of rainy season) with young tillers.
Management
During establishment, restrict traffic and livestock grazing. All sites should be allowed to establish the first year, prior to any grazing. Once grazing is started do not graze lower than 4 to 6 inches. Apply fertilizer according to soil test recommendations. Application of fertilizer may be split.
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
|---|---|
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Cold Stratification Required | Yes |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Drought Tolerance | High |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Fire Tolerance | High |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 180 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 180 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 200 |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 300 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | No |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | 22 |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Medium |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 60 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 18 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 18 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 30 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 16 |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Salinity Tolerance | Medium |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -18 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -18 |
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | -3 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 48 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Moisture Use | Low |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.5 |
| pH, Maximum | 7.6 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.0 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 50 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 48 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 5000 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Minim | 5000 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 19000 |
| Planting Density per Acre, Maxim | 19000 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.0 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.0 |
| pH, Minimum | 5.0 |
Morphology/Physiology
| Active Growth Period | Summer |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Toxicity | None |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Shape and Orientation | Decumbent |
| Shape and Orientation | Decumbent |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Color | Yellow |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Flower Conspicuous | No |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Dense |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Moderate |
| Bloat | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Active Growth Period | Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Summer |
| Active Growth Period | Summer |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Moderate |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Bloat | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Lifespan | Long |
| Lifespan | Moderate |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 5.0 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 5.0 |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 1.5 |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 1.5 |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Growth Form | Rhizomatous |
| Growth Form | Rhizomatous |
| Growth Form | Bunch |
Reproduction
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
|---|---|
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | Yes |
| Propagated by Sprigs | Yes |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
| Propagated by Seed | No |
| Propagated by Seed | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Slow |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Slow |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Rapid |
| Vegetative Spread Rate | Rapid |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Small Grain | No |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Seedling Vigor | Medium |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | Slow |
| Seed Spread Rate | None |
| Seed per Pound | 325000 |
| Seed per Pound | 325000 |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Period End | Fall |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Period Begin | Summer |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | None |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | None |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Commercial Availability | Routinely Available |
| Bloom Period | Mid Summer |
| Bloom Period | Mid Summer |
| Bloom Period | Mid Summer |
| Bloom Period | Late Summer |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
Suitability/Use
| Post Product | No |
|---|---|
| Post Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Graze Animal | Medium |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Post Product | No |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Protein Potential | Low |
| Protein Potential | Medium |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Veneer Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Nursery Stock Product | Yes |
| Palatable Browse Animal | Low |