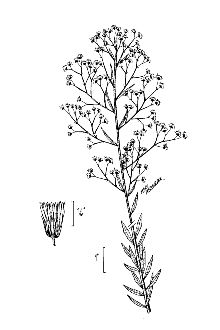
Canadian Horseweed
Scientific Name: Conyza canadensis (L.) Cronquist

| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Usda Symbol | COCA5 |
| Group | Dicot |
| Life Cycle | AnnualBiennial, |
| Growth Habits | Forb/herb |
| Native Locations | COCA5 |
Plant Guide
Alternate Names
Common Alternate Names: Horseweed, marestail, Canada fleabane Scientific Alternate Names: Erigeron canadensis
Ethnobotany
Canadian horseweed was used by numerous Native American peoples to treat a variety of ailments, Use soil moisture sensors to measure the soil moisture of Canadian Horseweed., It was used by the Seminole as a cough and cold medicine (Sturtevant, 1954), The Navajo and Chippewa used Canadian horseweed for stomach pain (Densmore, 1928; Wyman and Harris, 1951), and the Iroquois used an infusion of the plant to combat fevers (Rousseau, 1945),
Status
Please consult the PLANTS Web site and your State Department of Natural Resources for this plant’s current status (e.g., threatened or endangered species, state noxious status, and wetland indicator values).
Weediness
This plant may become weedy or invasive in some regions or habitats and may displace desirable vegetation if not properly managed. Please consult with your local NRCS Field Office, Cooperative Extension Service office, state natural resource, or state agriculture department regarding its status and use. Weed information is also available from the PLANTS Web site at http://plants.usda.gov/. Please consult the Related Web Sites on the Plant Profile for this species for further information.
Description
General: Canadian horseweed is a native winter or summer annual forb in the sunflower family. The plants are erect with one to several stems reaching 30 to 150 cm (1 to 5 ft) tall. Stems are typically unbranched at the base unless damage has occurred to the apical growing points. The leaves are linear to oblanceolate, 2 to 8 cm (0.8 to 3.1 in) long and 2 to 8 mm (0.08 to 0.31 in) wide. The leaf margins are ciliate-serrate. The inflorescence is a loose panicle. The numerous flower heads are very small, 2 to 4 mm (0.08 to 0.16 in) tall and 3 to 7 mm (0.12 to 0.28 in) wide. The rays are white or purplish (Welsh et al., 2003) and very small, only reaching 0.5 to 1.0 mm (0.02 to 0.04 in) in length (Cronquist 1994). The fruit is an achene with a white bristly pappus. There are approximately 700,000 seeds per pound (USDA-NRCS, 2012). Distribution: Canadian horseweed is native throughout much of North America. It was introduced into Europe in the mid 17th century, likely along with Canadian furs shipped to France. For current distribution, please consult the Plant Profile page for this species on the PLANTS Web site. Habitat: Canadian horseweed is common in grasslands and in moist disturbed sites including riparian and wetland areas. It has become a common pest in agricultural locations throughout its range.
Adaptation
Canadian horseweed is adapted to a broad range of conditions and soil types. It prefers slightly acidic to neutral soils (pH 4.8 to 7.2) in areas receiving 410 to
Establishment
Canadian horseweed has been described as both a summer annual and a winter annual with seed germinating at any time with sufficient moisture and warmth (Waggoner et al., 2011). In winter annual forms the seed germinates in the fall and the plant overwinters as a rosette. It then bolts in the spring and produces flowers in mid to late summer. Spring germinating Canadian horseweed spends relatively little time as a rosette before bolting (Loux et al., 2006). The seed (achenes) are small and light and can travel great distances in the wind. Dauer et al. (2007) reported seed of Canadian horseweed travelling at least 500 m (1,640 ft) from source populations.
Management
Canadian horseweed increases under reduced tillage and no-till situations (Steckel and Culpepper, 2006). Seed production and dissemination in disturbed areas can be reduced with mowing to reduce spread. Small occurrences can be controlled by pulling or roguing. For management of Canadian horseweed in agricultural situations, see “Control” below.
Pests and Potential Problems
Horseweed species can serve as a host for the tarnished plant bug (Lygus lineolaris), which can be a pest in alfalfa, cotton and other agricultural crops (Loux et al., 2006). Horseweeds can also be a host for the viral disease, aster yellows, which is transported to other plants via leafhoppers (Loux et al., 2006). Vegetation of Canadian horseweed contains a terpene which can be irritating in the nostrils of horses (Whitson et al., 1996). Canadian horseweed can reduce crop yields through direct competition for resources. Canadian horseweed is also known to contain allelopathic chemicals which can inhibit germination and reduce seedling growth in several species (Shaukat et al., 2003).
Environmental Concerns
Concerns
Concerns
Several herbicide resistant biotypes of Canadian horseweed have been discovered. In 1980, a Gramoxone (Paraquat) resistant biotype was first reported. In 1989, atrazine resistant biotypes were discovered in Belgium. Horseweeds resistant to the ALS (acetolactate synthase) family of herbicides were discovered in Israel in 1993 (Zheng et al., 2011). A glyphosate resistant horseweed was first reported in 2000 (VanGessel, 2001). Since that time, glyphosate resistant Canadian horseweed has been found in much of the U.S., Europe and Asia (Heap, 2012).
Control
Canadian horseweed is easier to control when plants are young (less than 2 inches tall). Control efforts should be concentrated in late fall and early spring when plants are young. The most effective treatment for controlling Canadian horseweed is 2, 4-D ester or a combination of 2, 4-D ester plus glyphosate (Loux et al., 2012). Herbicide treatments with residual activity to control later emerging horseweed are also recommended. Plants not killed by chemical burn down will re-grow and be less susceptible to later herbicide applications. These plants often sprout multiple stems resulting in increased seed production. In populations with a resistant biotype, chemical treatments should contain three or more herbicides (Loux et al., 2006). Three-way mixture of glyphosate, 2, 4-D ester, plus chlorimuron or cloransulam are recommended. Please contact your local agricultural extension specialist or county weed specialist to learn what works best in your area and how to use it safely. Always read label and safety instructions for each control method. Trade names and control measures appear in this document only to provide specific information. USDA NRCS does not guarantee or warranty the products and control methods named, and other products may be equally effective.
Seeds and Plant Production
Plant Production
Plant Production
Cultivars, Improved, and Selected Materials (and area of origin) None
References
Cronquist, A. 1994. Asterales. In: Cronquist, A., A.H. Holmgren, N.H. Holmgren, J.L. Reveal and P.K. Holmgren (eds). 1994. Intermountain flora: Vascular plants of the Intermountain West, U.S.A. Vol. 5. Bronx, New York: The New York Botanical Garden. 496 pp. Dauer, J.T., Mortensen, D.A., and M.J. Vangessel. 2007. Temporal and spatial dynamics of long-distance Conyza canadensis seed dispersal. Journal of Applied Ecology. 44: 105-114. Densmore, F. 1928. Uses of plants by the Chippewa Indians. SI-BAE Annual Report No. 44: 273-379. Heap. I. 2006. The International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds. www.weedscience.com (accessed August 27, 2012). Loux, M.M., Stachler, J.M., Johnson, W.G., Nice, G.R.W. and T.T. Bauman. 2012. Weed Control Guide for Ohio Field Crops. Ohio State University Extension. Bulletin No. 789. URL. http://ohioline.osu.edu/b789/index.html (accessed 28Aug2012). Loux, M., Stachler, J., Johnson, B., Nice, G., Davis, V., and D. Nordby. 2006. Biology and management of horseweed. The glyphosate, weeds and crops series. Purdue University Extension. GWC-9. 12p. Regehr, D.L., and F.A. Bazzaz. 1979. The population dynamics of Erigeron canadensis, a successional winter annual. Journal of Ecology. 67: 923-933. Rousseau, J. 1945. Le Folklore Botanique De Caughnawaga. Contributions de l’Institut botanique l’Universite de Montreatl. 55: 7-72. Shaukat, S.S., Munir, N., and I.A. Siddiqui. 2003. Asian Journal of Plant Sciences. 2(14): 1034-1039. Steckel, LE. and S. Culpepper. 2006. Impacts and management of glyphosate-resistant weeds in the southern region. National IPM Conference 46.4. [Proceedings]. [USDA NRCS] USDA Natural Resources
Plant Traits
Growth Requirements
| Temperature, Minimum (°F) | 52 |
|---|---|
| Adapted to Coarse Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Fine Textured Soils | Yes |
| Adapted to Medium Textured Soils | Yes |
| Anaerobic Tolerance | Low |
| CaCO3 Tolerance | Low |
| Cold Stratification Required | No |
| Drought Tolerance | Low |
| Fertility Requirement | Medium |
| Fire Tolerance | Low |
| Frost Free Days, Minimum | 60 |
| Hedge Tolerance | None |
| Moisture Use | Medium |
| pH, Maximum | 7.2 |
| pH, Minimum | 4.8 |
| Precipitation, Maximum | 55 |
| Precipitation, Minimum | 14 |
| Root Depth, Minimum (inches) | 6 |
| Salinity Tolerance | None |
| Shade Tolerance | Intolerant |
Morphology/Physiology
| After Harvest Regrowth Rate | Slow |
|---|---|
| Toxicity | None |
| Shape and Orientation | Erect |
| Nitrogen Fixation | None |
| Resprout Ability | No |
| Active Growth Period | Spring, Summer, Fall |
| Bloat | None |
| C:N Ratio | Medium |
| Coppice Potential | No |
| Fall Conspicuous | No |
| Fire Resistant | No |
| Flower Color | White |
| Flower Conspicuous | Yes |
| Foliage Color | Green |
| Foliage Porosity Summer | Porous |
| Foliage Texture | Coarse |
| Low Growing Grass | No |
| Leaf Retention | No |
| Known Allelopath | No |
| Height, Mature (feet) | 5.0 |
| Growth Rate | Rapid |
| Growth Form | Single Crown |
| Fruit/Seed Conspicuous | No |
| Fruit/Seed Color | Brown |
| Foliage Porosity Winter | Porous |
Reproduction
| Vegetative Spread Rate | None |
|---|---|
| Small Grain | No |
| Seedling Vigor | High |
| Fruit/Seed Persistence | No |
| Seed Spread Rate | Rapid |
| Seed per Pound | 700000 |
| Propagated by Tubers | No |
| Propagated by Sprigs | No |
| Propagated by Sod | No |
| Propagated by Cuttings | No |
| Propagated by Corm | No |
| Propagated by Container | No |
| Propagated by Bulb | No |
| Propagated by Bare Root | No |
| Fruit/Seed Abundance | High |
| Commercial Availability | No Known Source |
| Bloom Period | Indeterminate |
| Propagated by Seed | Yes |
Suitability/Use
| Veneer Product | No |
|---|---|
| Pulpwood Product | No |
| Post Product | No |
| Palatable Human | No |
| Nursery Stock Product | No |
| Naval Store Product | No |
| Lumber Product | No |
| Fodder Product | No |
| Christmas Tree Product | No |
| Berry/Nut/Seed Product | No |